A simple car shock alarm circuit I have I have explained in this article can eb effectively used to alarm the owner each time the car comes across some kind of vibrational intrusion ether from a potential theft of simply a damaging hit from an external source.
Introduction
Today most of the cars are equipped with this type of security feature where an alarm is raised in an event of a shock or a hit made over the car body.
In this article I have explained a very simple and cheap car shock sensor alarm circuit which costs hardly 1/2 a dollar yet performs the actions reasonably accurately.
The working Principle of the Shock alarm.
The principle employed here is pretty basic, a mic is used to sense the impact, the sensed output is amplified by a transistorized amplifier.
How the Circuits Works
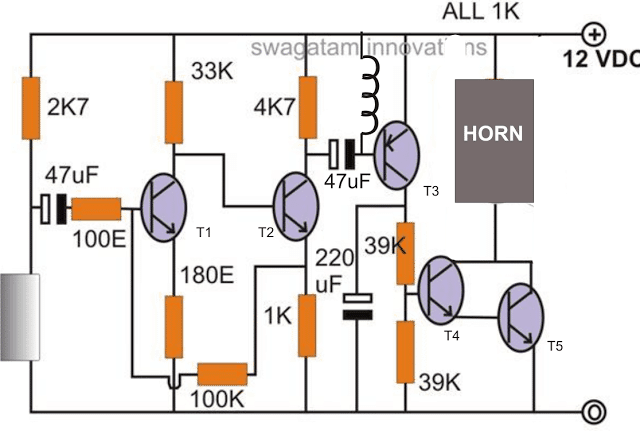
Looking the circuit diagram, the whole functioning can be understood with the following points:
The mic stage consists of the mic itself, the biasing 2k7 resistor and the 47uF coupling capacitor.
T1 and T2 form the first amplifier stage and is the heart of the circuit.
The feedback 100K resistor plays an important function of keeping the amplification sustained at a stable rate.
When a shock impact is sensed by the mic, it converts the shock vibrations into tiny electrical pulses.
T1 and T2 work like a preamplifier, and amplifies the MIC response into a reasonably high electrical pulse, sufficient for driving the power output stage transistor T3 saturation.
The T3 responds to the above signal and activates the connected alarm siren, alerting the folks around regarding the possible theft attempt.
One big drawback of this cheap car shock alarm circuit is that it cannot distinguish between physical shocks and shock waves developed due to loud bangs or noises.
Parts List
- R1 = 5k6
- R2 = 47k
- R3 = 3M3
- R4 = 33K
- R5 = 330 OHMS
- R6 = 2K2
- C1 = 0.33uF/400V
- C2 = 4.7uF/25V
- T1, T2 = BC547
- T3 = TIP127
- D1 = 1N4007
- Siren = Any 12 V car siren
Pendulum Type Shock Alarm
The circuit may be implemented to safeguard automobiles, big items, houses and other sites since the sensor enables you to detect any kind of motion. This gadget may also be used for many technological tests.
The relay can easily power high wattage audio or alarm devices, for example sirens, horns, lights, etc.
Standby current consumption is extremely low (around 100 uA) during the time the relay is in the deactivated state, which increases the battery-life.
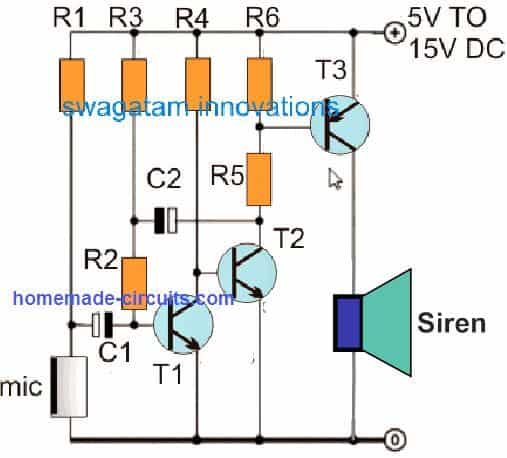
The schematic diagram of the Pendulum shock Alarm is shown in Figure below.
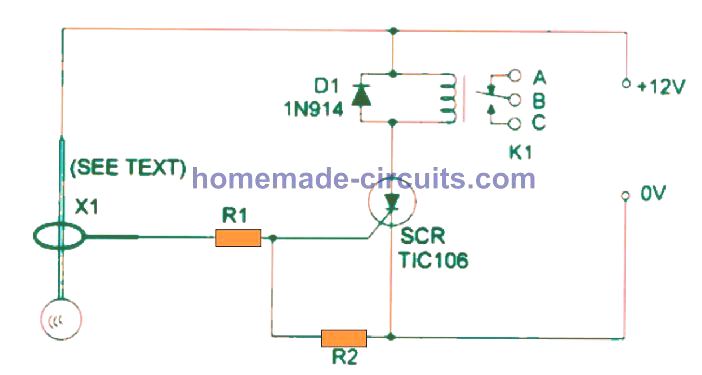
The circuit is centered around an SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier), that powers ON the relay whenever the sensor picks up any kind of movement.
Relay coil voltage is determined based on the power supply voltage.
You may use a small DPDT 1A Mini Relay or, for hefty loads, a 10A mini SPDT relay. These types of relays are usually rated at 12 VDC and consume not more than 38 mA.
Once initiated, the circuit will be latched permanently, in order to reset the circuit, or stop the alarm can be made a small push to ON switch may be wired between the SCR anode and cathode.
The leads of the polarized component like the SCR and diode, should be carefully noted and assembled with correct polarity.
Parts List
SCR -TlC106 or SCR
D1 - 1N914 or 1N4148
K1 - 12V relay (see text)
S1 - SPST toggle switch
Rl - 22k, 114W,5% resistor
R2 - 10k, 114W,5% resistor
X1 - Pendulum sensor
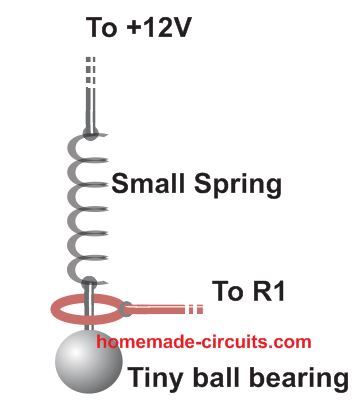
Pendulum Shock Sensor Assembly
The pendulum sensor is a simple homemade mechanism built using a small ball pen spring, a small steel ball as the load, from any ball-bearing system, and connecting copper wires as shown in the following figure.
Make sure to use a spring that is very delicate and stats swinging even with slightest of jerk or shock.


With over 50,000 comments answered so far, this is the only electronics website dedicated to solving all your circuit-related problems. If you’re stuck on a circuit, please leave your question in the comment box, and I will try to solve it ASAP!