The following calculator calculates the voltage drop and voltage at the end of the wire for American Wire Gauge from 4/0 AWG to 30 AWG, aluminum or copper wire. (Note: It just calculates the voltage drop, consult the following table for rules-of-thumb or your local or national electrical code or your electrician to decide what is legal!) Note that the voltage drop does not depend on the input voltage, just on the resistance of the wire and the load in amps.
Voltage Drop Calculator
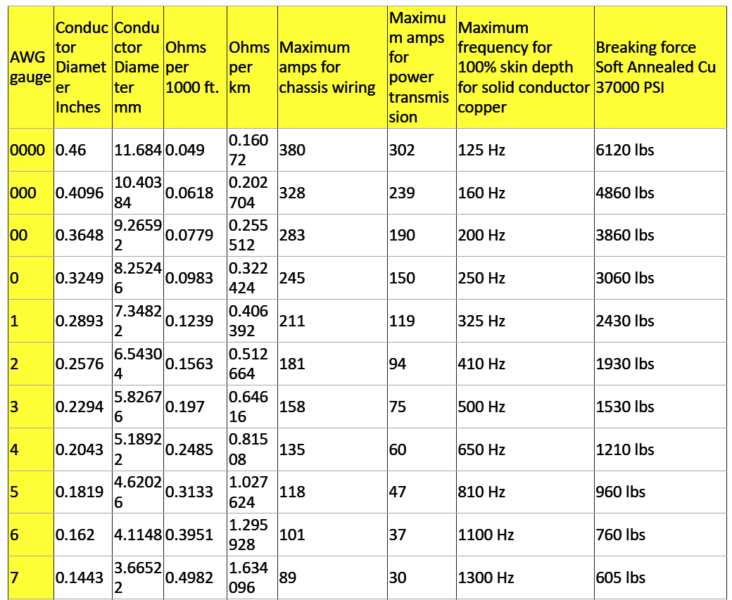
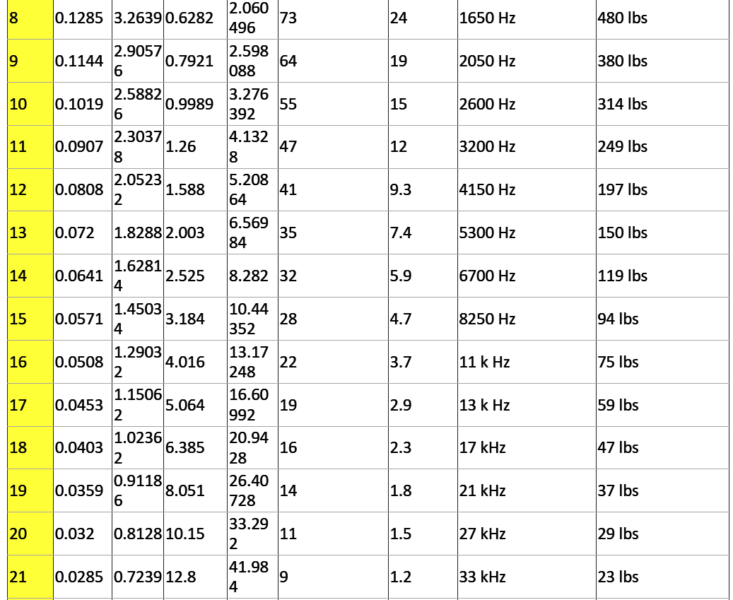
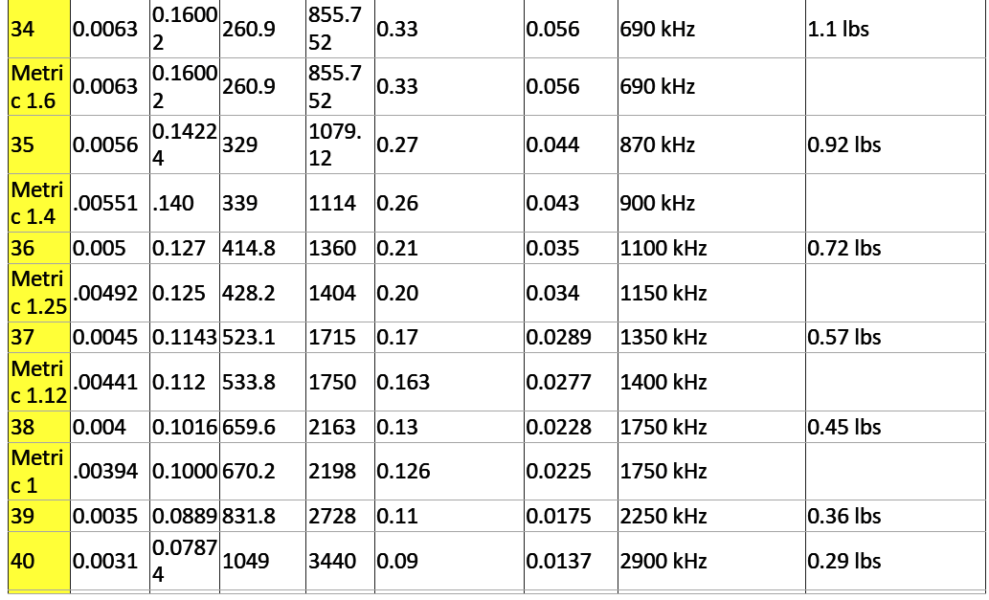
AWG: In the American Wire Gauge (AWG), diameters is generally computed by utilizing the formula D(AWG)=.005·92((36-AWG)/39) inch. For the 00, 000, 0000 etc. gauges you choose -1, -2, -3, helping to make more sense mathematically rather than "double nought." Therefore in American wire gage each 6 gauge drop delivers a doubling of the wire dimension, and each 3 gauge reduction doubles the wire cross sectional area. Much like dB in signal and power ranges. An anticipated yet precise sort of this formula donated by Mario Rodriguez is D =.460 * (57/64)(awg +3) or D =.460 * (0.890625)(awg +3).
Metric Wire Gauges (check tablebelow)
Metric Gauge: In the Metric Gauge scale, the measure is 10 times the dimension in millimeters, therefore a 50 gauge metric wire is likely to be 5 mm in size. Remember that in AWG the diameter increases as the gauge decreases,
however for metric gauges it happens to be the reverse. Maybe for this confusion, normally metric sized wire is designated in millimeters instead of metric gauges.
Current Holding Specs (refer to table below)
Definition: Ampacity is the current carrying capability of a cable. Put simply, how much amps it may be rated to carry? The following list is a manual of ampacity or copper wire current holding capability following the Handbook of Electronic Tables and Formulas for American Wire Gauge. While you may speculate, the rated ampacities are simply a general guideline. In mindful engineering the voltage drop, insulation temperature limit, thickness, thermal conductivity, and air convection and temperature ought to all be evaluated. The Highest Amps for Power
Transmission makes use of the 700 circular mils per amp principle, that could be extremely traditional. The Highest Amps for Chassis Wiring just happens to be a traditional evaluation, nevertheless will suit electrical wiring in air, and not in a bundle. For short measures of wire, for example is employed in battery packs you might want to substitute the resistance and load current with dimensions, weight, and flexibility. Please note: For installations that might want to comply with the National Electrical Code, one should work with their recommendations. Contact your neighborhood electrician to really know what is lawful!
Highest Frequency for 100% Skin Depth
This information is ideal for high frequency AC engineering. Whenever high frequency AC is involved in a wire you can find a likelihood for the current to run around the periphery the wire. This raises the overall resistance. The frequency detailed in the table exhibits the frequency where the computed skin depth is comparable to the radius
of the wire, which is a manifestation that above this frequency you probably should start contemplating the skin effect while determining the wire's resistance.
Busting Force for Cu Wire
This approximate relies upon nick-free soft annealed wire bearing a tensile strength of 37000 pounds per square inch.

The next simplified wire current calculator gives us the minimum wire gauge needed for an inductor based on current carrying capacity, when we consider a standard current density of 3 A/mm², which is common for copper wires in power electronics.
Inductor Wire Thickness Calculator
This calculator determines the minimum required wire thickness for an inductor, assuming a current density of 3 A/mm² for copper wire.
Results:
| Required Wire Area | Wire Diameter |
|---|---|
| 0 mm² | 0 mm |
How to Use the Calculator
- Enter Inductor Current (in Amps) – This is the current the inductor will handle.
- Click "Calculate" to get:
- Minimum Required Wire Cross-Sectional Area (mm²).
- Wire Diameter (mm) for proper current handling.
What is the difference Between Minimum Required Wire Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) and Wire Diameter (mm)
Minimum Required Wire Cross-Sectional Area (mm²):
This tells us about the total cross-sectional area of the wire, measured in square millimeters (mm²).
It gives us how much current the wire can safely carry without overheating.
You can calculate it using the following formula:
A = I / J
Where:
A = Required wire cross-sectional area (mm²)
I = Inductor current (Amps)
J = Current density (Amps per mm²) (typically this is 3 A/mm² for copper wire in power circuits)
Wire Diameter (mm) for Proper Current Handling:
This provides us the physical thickness of the wire which is measured in millimeters (mm).
You can calculate it based on the cross-sectional area using the same formula used for a circle:
d = sqrt((4 * A) / π)
Where:
d = Wire diameter in mm
A = Cross-sectional area (mm²)
π = 3.1416
But Why Do We Need Both the parameters?
Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) tells us how much current the wire can handle.
Wire Diameter (mm) tells us the actual physical size of the wire that we need to use.
If we only use diameter then we might pick a wire that is too thin for the required current.
If we only use cross-sectional area then we might not know the actual wire thickness.
Example Calculation:
If Inductor Current = 10A and Current Density = 3 A/mm²:
Cross-Sectional Area:
A = 10 / 3 = 3.33 mm²
Wire Diameter:
d = sqrt((4 * 3.33) / 3.1416)
d = sqrt(13.32 / 3.1416)
d = sqrt(4.24)
d = 2.06 mm
So we need a wire with at least 3.33 mm² cross-sectional area which means we should pick a wire of diameter ≈ 2.06 mm.