As electronics enthusiasts we may come across many kinds of resistors, from small fixed resistor to high current bulk rheostat. There are humongous classifications among resistors, but here we will focus on a particular kind of resistor called “flex resistor” and learn how it works.
As the name signifies a flex resistor is flexible and also changes its resistance when it gets bend. This sensor device is boon for those who may be working in the field of robotics, medical devices, angular displacement measurement, motion sensing game development, etc.
There are limitless numbers of applications if you peak your imagination to maximum.
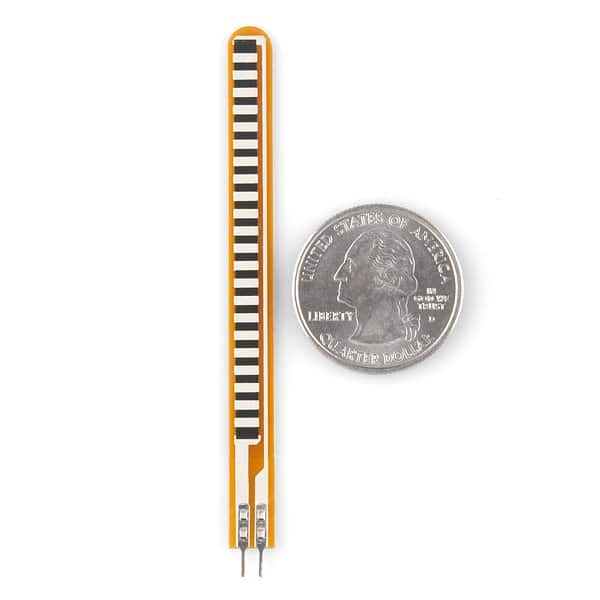


Flex resistor compared with a coin.
Specifications overview:
The flex resistor measures 2.2 inch on length (may vary), having a resistance around 10K ohm when it is flat and has a huge tolerance range of +/- 30%. This means if you bought two similar flex resistances, its resistance to angular bend ratio may vary a bit. This parameter must be considered when you calibrate your design.
It has working temperature range of -35 degree to +80 degree Celsius. It has power rating of 0.5 watt continuous and 1 watt peak. The predicted life cycle is greater than 1 million times.
There is bend limit for every flex resistor please check the data sheet for the respective flex resistors; if you exceed those limits you may damage your flex resistor.
There are two classifications of flex resistor:
1) Unidirectional
2) Bidirectional
Unidirectional: This type of flex resistor can be bent only in one direction within their bend limit. If we do the same on the other direction, we may damage it.
Bidirectional: This resistor can be bent on either direction within their bend limit.
So, choose the right flex resistor depending on your application.
How Flex Resistors work?
There is a conductive ink sandwiched between two plastic films. Electrodes are placed either sides of conductive ink. The conductive ink consists of microscopic particles which are electrically conductive.
When the resistor is flexed the microscopic particles move away from each other, and the resistance increases. Vice versa is also true.
Basic schematics on how to use:
Here is a basic schematic of a flex resistor application.
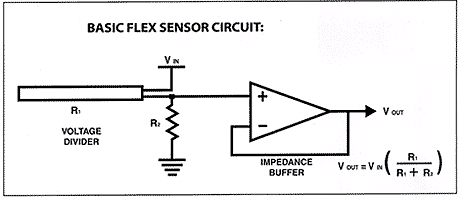
The flex resistor has limitless applications if you know how to use them. Here is a simple op-amp circuit paired with a flex resistor. You can set threshold to trigger the output, if you use an op-amp in comparator mode. The suggested op-amps are LM324 and LM358; you may also give a try for 741.
You can also pair it with arduino, by giving the flex resistor to analogue read pin of arduino with pull down resistor. No additional libraries are required.
Arduino Interface
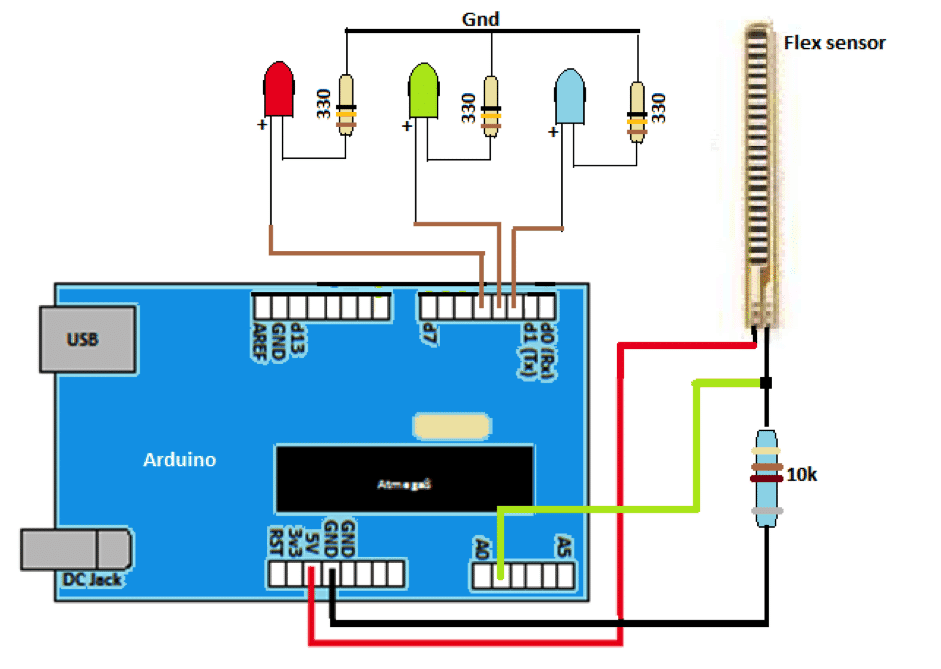
Here is an illustration of simple angle sensing for flex resistor. If the flex resistor is flat, blue LED illuminates, if the resistor is flexed to an angle x (say) green LED illuminates, if it flexes greater than x then, red LED illuminates.
Flex resistors can be also seen in applications which demand simulation of complex movements and patterns, for example it's used for studying precise human finger movements, where the motion of the finger is tracked by flex resistor, decoded and displayed on a screen. This principle may be adapted by game developers to develop motion based game.
Conclusion:
Through this simple electronic component, we find huge spectrum of applications. There is no limitation to deploy the component on our daily used electronics, the only limitation may be in our imagination to deploy those in the right way.
categized the angler measurement devices with the use of flexible resistors
I will immediately grab your rss as I can not find your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Thank you, you can find the subscription link just under the article posts.