In this post I have explained regarding how a PNP transistor works or conducts in response to a fixed biasing voltage and a varying supply voltage, across its base and emitter. The question was put forth by Mr. Aaron Keenan.
Question Regarding PNP BJT Working
Great information and lots of interesting circuits!
I have a question about a specific circuit on the page above.Here's the exact circuit.

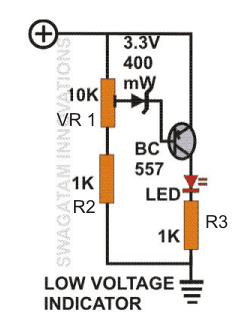
I'm going a little crazy trying to figure out exactly how it works to trigger at a low voltage threshold. I graduated Electrical Engineering in 2004, I guess I've gotten rusty and would really appreciate if you could help explain?
Here's what I understand: - The circuit acts purely like a voltage divider until the voltage at the point between VR1 and R2 is aproximately 3.3v lower than the voltage at the base of the transistor.
At which point the zener conducts in reverse and the transistor conducts (illuminating the diode).
The voltage at the base of the transistor is aproximately 0.7 volts (Vbe) lower than the input (emitter) As an example, if the source voltage is 12 volts:Assume Vbe = 0.7 12v - 0.7 - 3.3 = 8v
The voltage divider would have to be 4 Volt drop across VR1 (min) and 8Volts across R2 (maximum) in order for the transistor to conduct.
Let's set VR1=1K (4v drop) and R2=2K (8v drop) What I don't understand is that if the voltage increases (ie. from 12 to 36) then I would expect the light to go off (since the circuits purpose is for the light to come on when the voltage is low).
However, increasing the source voltage would only increase the difference in voltage across the zener (ie. futher exceeding its breakdown voltage) and the light would continue to stay on. For example, at 36 Volts :VR1 voltage drop = 12R2 Voltage drop = 24.
Since we have 36 - 0.7 = 35.3 volts at the base and 24 Volts across R2 we have further exceeded the breakdown voltage and the light is still on.
If I decrease the voltage to 6 Volts:VR1 voltage drop = 2 Volts R2 voltage drop = 4 Volts
Since we have 6 - 0.7 = 5.3 at one end of the zener and 4 Volts at the other, the breakdown voltage of the zener was not exceeded and therefore the light is off.
I'm not one to just use circuits blindly and would like to fully understand how it works. Could you be so kind as to put me on the right track? I'd really really appreciate it!! (2 days I can't sleep trying to figure it out!)
Thanks again!Aaron
Solution (as per my assumption and derivation):
How a PNP Transistor Actually Works
Thanks Aaron,
To learn how PNP transistors work can be a little confusing due to their opposite course of actions compared to their NPN counterparts.
I'll try to explain the functioning with a simple cross multiplication which is derived as per my understanding: Let's remove R2 and the zener to make the simulation easier.
Let's assume, with a 12V supply we adjust the preset to produce 0.6V across base/emitter of the transistor.
This lights up the LED brightly.
From here on if we increase the voltage the 0.6V across B/E of the transistor can be expected to drop and making the conduction difficult for the transistor and correspondingly reduce the brightness level on the LED.
The trick here is to consider an inversely proportional calculation instead of a directly proportional calculation which might be true for an NPN transistor but not for a PNP.
The following formula can be tried for verifying the results:
12/V = b/0.6
Here 12 refers to the threshold voltage level at which the preset is adjusted to achieve 0.6V across B/E of the transistor.
V is the "test" voltage level which may be higher than 12V, b is the change in the B/E voltage in response to the applied higher "test" voltage.
So let's take 36V as per your suggestion for the expression V, solving the above formula with 36V we get
12/36 = b/0.6
36 x b = 12 x 0.6
b = 0.2V
At 0.2V the transistor will be completely shut off.
This is how I assume the calculation to be, and how a PNP might conduct in response to a set base/emitter voltage and a rising supply voltage
Please feel free to investigate and respond on the above assumption.
Sir, My quaries is
12 volt 75 wp solar panel 12 volt 18 watt led and and 12volt 75ah battery then what will be combination of reasitance value and which transistor i will use ?
Rakesh. you will need to add a current limiter as explained in the following article.
you will need an LM338 IC for this
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2013/06/universal-high-watt-led-current-limiter.html
sir how r u i need lm196 ic where i purchases pl give me add. or price
thankyou
shuddhatam jain
shuddhatam, you can try it it Lamington Road in Mumbai, I don't know about the price
thanks for reply & best suggestion. i 'd read the article u suggested. i 'll like to say sorry for i 'd not mentioned the working voltage that i expecting. that is 3.6 – 4.2V so that any one can easily construct the emergency lamp with the help of spare mobile battery.
i think u understand the problem.
the suggested idea will work with a 4V battery also without any significant modifications, except may be the 33k resistors which might lowered to 10k…and the diodes at the collector of the power transistor which could be completely eliminated
Thank u for this interesting article. pls add an article on emergency lamp using single pnp transistor which can disconnect load LED at low battery & presence of mains. i would be greatful to u if the circuit should contain only 4-5 components other than transistor. the components should be low cost & easily available in local store or junk box.
thank u once again.
It's my pleasure!
You can try the fourth circuit from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2011/12/how-to-make-efficient-led-emergency.html
just add an additional BC547 with the right most BC547 to make a Darlington configuration.
Do the same with the BC557 using another BC557 with it
these modifications will ensure perfect results from the respective stages.