In this article I have explained a simple method through which large amounts of oxygen and hydrogen could be generated at home using an ordinary electrical setup, and very cheaply.
Before I have explained the actual process, it would be important to read the following points related to the experiment:
Warning: The simple concept of generating pure oxygen at home using 220 V or 120 V mains AC presented here may look simple, but since it employs a direct non-isolated mains AC, the set up can be extremely dangerous to touch in an uncovered position. Therefore, the experiment is absolutely NOT recommended for people who are new to electrical experiments and do not know how to safeguard themselves from electrical hazards.
Do not use the oxygen from this set up for treating of sick people. The author of this website takes no responsibility for any mishap or accidents due to inappropriate use of this experiment.
Advantages
Although the experiment may not be safe for a layman, there are some distinct advantages of this particular concept:
If the whole set up is implemented with appropriate care and caution.... and with appropriate installations, the unit can give you unlimited amounts of oxygen ( and hydrogen) from two most basic elements available at home, which are tap water and mains AC power.
Due to the use of high voltage (220V/310V) the current consumption is less and the output is more which makes the system cheaper than the other concepts.
How to Enhance the Process
Bringing the electrodes nearer will cause aggressive generation of the gases, across the respective electrodes.
Hugely aggressive output generation can also be expected if a drop of H2SO4 is added to the water, although the main objective of using 220 V is to avoid using external catalyst.
Due to the use of 220V, the temperature of water might increase slightly, which may automatically help to enhance the production process, since higher temperature of water is supposed to increase the efficiency rate of the electrolysis process.
Importance of Oxygen and Hydrogen
We all know the potentials of these two gases and how important they are on this planet.
Oxygen is the life sustaining gas without which no living creature on this planet can live.
Hydrogen on other hand has its own merits and can be considered as the future fuel which would ultimately power our vehicles and cook our foods once all the naturally available fossil resources goes out of stock and gets depleted.
What is Electrolysis of Water
In school days we all have learned and witnessed the process called the electrolysis of water, where water which is made up of two main constituents H2O (two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen) is broken down forcibly with the help of electric current.
However in this process, normally a pinch of salt is added or sometime a drop of sulfuric acid is added for enhancing the electrolysis process.
This results in speedy electrolysis process, and we are able to see large and thick amounts of gas bubbles come out across the two electrodes which are connected to a potential difference source or simply to a battery.
However there's an misconception that the above process generates oxygen and hydrogen with ease, in fact that may not be the case and if we carefully assess the process you will find it's not the water but the added chemical which is getting broken in the influence of the electric current.
That means if we add salt to water, the electrolysis process will generate the gas chlorine and sodium deposits over the two electrodes and not oxygen or hydrogen.....you can expect the generation of H and O, but in very negligible volumes.
For generating pure oxygen and hydrogen through the process of breaking down water components we need to implement the process of electrolysis without the addition of any foreign chemical into water. However, adding a very small quantity of H2SO4 or sulphuric acid could be added to enhance the process to a great extent. Make sure the quantity is correctly calculated, else it may lead to massive bubbling or even explosions in the water.
Simply put, the procedure must be carried out breaking H2O directly without the help of any catalyst medium.
However if you try to do this, you will find the process to be very lethargic and absolutely impossible, because the bond between the H2O components are so great, it might become impossible to disintegrate them into parts.
But it can be done through brute force, meaning instead of using low power DC, if we use mains AC, and introduce it into a container filled with water, we might just be able to force the liquid to separate into its pure forms.
THIS METHOD OF ELECTROLYSIS OF PURE WATER USING PULSED 220 V WITHOUT ANY CATALYST HAS BEEN DISCOVERED BY ME, I ASSUME SO, BECAUSE IT'S NOT BEEN DISCUSSED ANYWHERE ELSE ON THE NET SO FAR.
Why Use a High Voltage AC instead of Low Voltage DC
Technically, a 1.4 V DC is the ideal power for breaking water molecules into HHO. Anything above this is considered a waste of energy.
However, using 1.4 V would demand a heck lot of current and the electrodes will need to be placed very close to each to other, making the set up extremely infeasible at home for any lay person.
Using 220 V DC may look highly inefficient in electrical terms, but if you test it practically it turns out to be quite efficient due to the following reasons:
- 220 V or 120 V is easily accessible in our homes. Making a bridge rectifier is also very easy.
- Bridge rectifier converts AC into 100 Hz or 120 Hz pulses which enhances the electrolysis process significantly, compared to the specified 1. 4 V DC.
- The heat dissipation can be easily optimized by decreasing the electrode cross-sectional area, and distance between the electrodes.
- Using tap water means high water resistance, which in turn allows less current to be used.
- This also means less HHO production but practical results show that the process produces a continuous bubbling across the electrodes, yet the water staying at normal temperatures.
The above factors ensure that a 220 V approach is much efficient in many other ways compared to using a 1. 5 V DC.
Easy set up for Generating Oxygen and hydrogen at Home in Large Quantities
OK, the method is as simple as it can be, while experimenting I found that by converting mains AC to DC, the process aggravates more rapidly and thick fogs of gases can be seen across the respective electrodes.
And it is definitely important to use DC. otherwise the gases will alternately produced over the two electrodes haphazardly completely ruining the results.
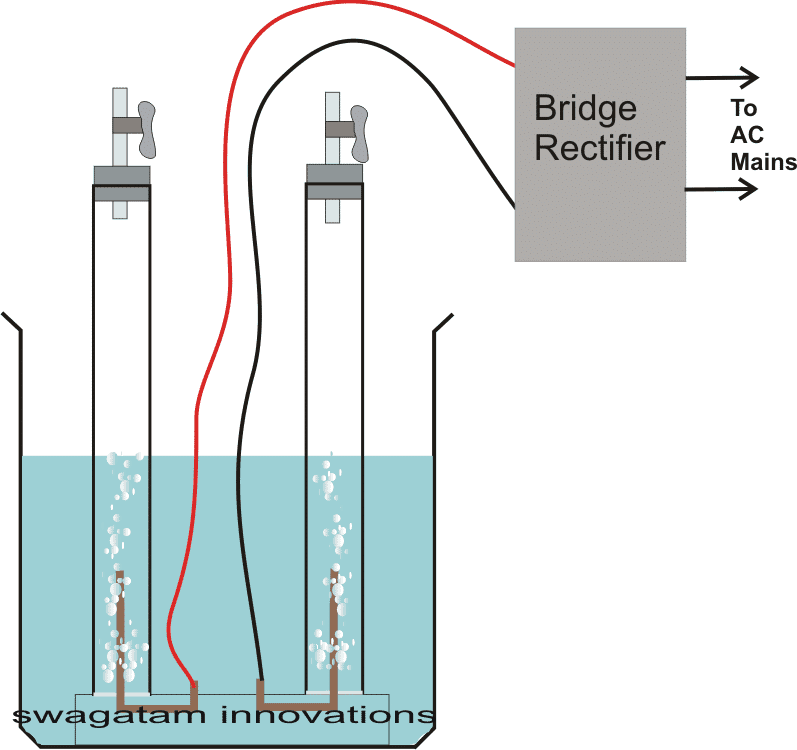
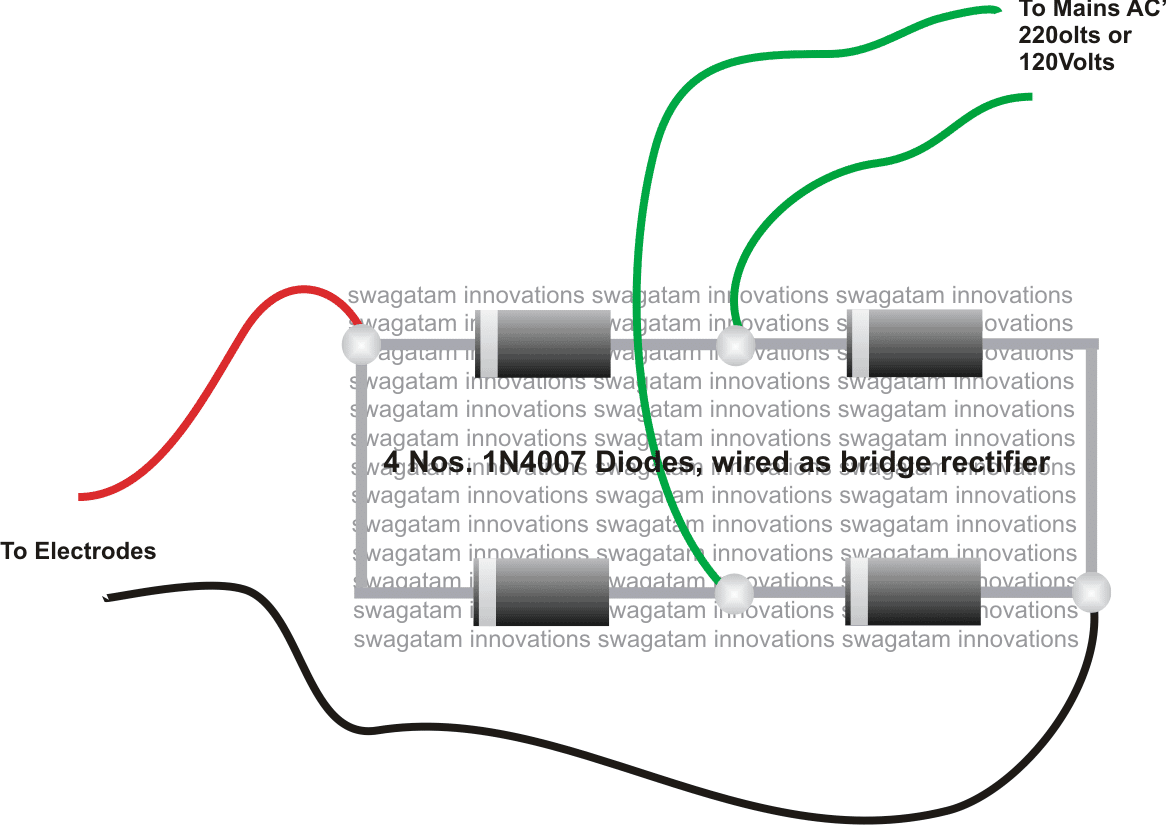
So....it's all about making a bridge rectifier circuit using four diodes, 1n4007 will do. take four of them and construct the bridge rectifier module and next wire up the system as per the shown diagram.
The glass apparatus will need to be carefully set. As can be see in the figure, the two glass tubes are inverted inside a container filled with water.
The two tubes should be filled with the water such that both the tubes share the container water among themselves.
A couple of GRAPHITE electrodes are fitted in such a way that they get inside the tubes water content just as shown in the figure.
The electrodes are terminated out through respective wires connections which are further connected to the bridge rectifiers positive and negative outputs.
The bridge rectifier inputs are in turn connected to mains AC.
The moment power is switched ON, thick surfs of bubbles can be seen coming out from the electrodes and exploding into the respective gas forms into the vacant area of the tubes.
No External Catalyst used
Since there's no external chemical involved here, we can be sure that the gas formed and collected inside the tubes to be pure oxygen and hydrogen.
As the process is allowed to continue, you will find the water level gradually coming down and getting transformed into oxygen and hydrogen within the two tubes.
The tubes should have a valve type arrangement at their top termination, so that the accumulated gas can be either transferred to a larger container or directly accessed from the nozzles by releasing the taps or the valve mechanism.
Video Clip show the minimum set up required for the electrolysis process:
How to construct the bridge rectifier and wire it for the above apparatus:
Increasing Oxygen Production through Series Connections
Since technically, only 1.4 V is required for an efficient implementation of electrolysis, implies that the 220 V could be divided into a number of series arrangements for multiplying the production rate of oxygen to many folds, as shown in the following example set up.
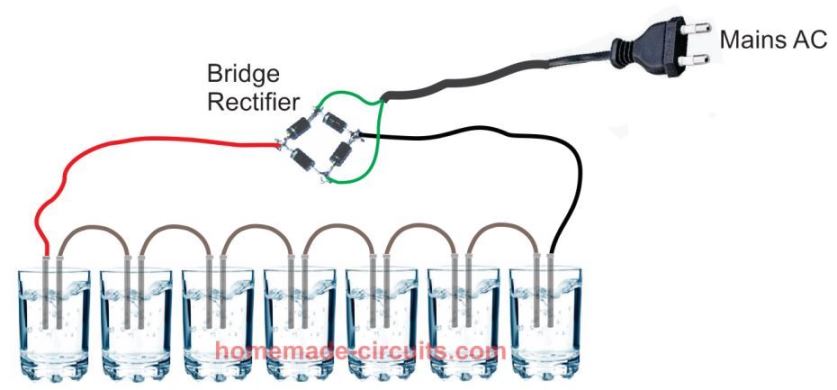
Here, we find that each glass/electrode set up is able to produce its own share of oxygen and hydrogen, thus making the total production 7 times higher. Actually, with a 310 v supply (after 220 V rectification), the above setup can be increased to 310 / 1.4 = 221 apparatus's, generating 221 times more oxygen than a single apparatus which was shown in our first example. That looks awesome, isn't it.
Remember the electrodes are graphite electrodes to avoid corrosion and oxidation. And, the water is pure tap water, no catalyst in the form of salt, acid, or baking soda must be used, which may otherwise cause false and dangerous outcomes.
Note: Although we all know that electrolysis of water generates oxygen and hydrogen, the gases coming out from the above set up has not been verified practically in a laboratory, so please make sure to test it on a small scale first, to confirm its efficacy.
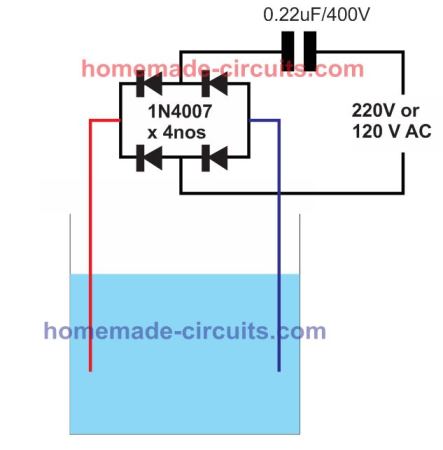
Increasing the Efficiency Rate by using nano pulse.
The results are not yet confirmed by me, but research has shown that decreasing the pulse width can further increase the efficiency of the electrolysis. It is called nano pulse electrolysis.
Perhaps the easiest way of implementing a nano pulse could be to put a capacitor in series with the AC input, as shown in the following figure:
What the capacitor does is it allows only a short, narrow, peak pulse to appear across the electrodes, causing the oxygen, hydrogen production to increase to much higher levels compared to any other conventional set up.
Warning
THE WHOLE SYSTEM INVOLVES HIGH AC AND DC POTENTIALS, DEATH CAN COME WITHIN MINUTES IF ANY OF THE PART OF THE SYSTEM IS TOUCHED, EVEN THE WATER IS HIGHLY DANGEROUS TO TOUCH IN SWITCHED ON POSITION. DO NOT SHORT CIRCUIT THE ELECTRODES, WHICH MAY RESULT IN FIRE AND HUGE EXPLOSIONS. GREAT CAUTION MUST EXERCISED WHILE HANDLING THIS SET UP.
USE OF A 100 WATT SERIES BULB IS RECOMMENDED TO AVOID AN ACCIDENTAL SHORT CIRCUIT, AND FIRE HAZARD SITUATIONS.
DO THIS AT YOUR OWN RISK.
Come across your web. Thanks. My 2 cents, for my beloved fishes.
1. I use coiled copper wire instead of carbon rod from Zn battery. Simply coiling the SWG 22 around the round object that’s 1 cm narrower than the collection bottle. The length of the coil is up to the submerged part of the bottle. The more wire-water contact surface = the more efficiency.
After a period of test, I thinly gold-plates it (with the help from the small service shop @$20). The la$t change is using gold wire, heh-heh. After a year, the gold wire’s weight is still the same but the sale price is 2 times more. What the benefit.
2. A cheap 5 V fan (from the old computer PSU) over the H2 electrode helps dispersing of the highly flammable H2.
3. Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) is the perfect electrolyte. The produced O2 has no sulfur in it.
4. The last modification is using 2*30,000 mAh power banks(PB) instead of direct power from the main. The 5V DC from it is 100% safe. A simple timer + relay (@ both the AC & DC wire) alternates the PB between charged service. The being charged one is cut out from the electrolytic tank, thus the absolute safety.
Note : the AC relay is reed switch to ensure 100% isolation. Circui driving current is from the serviced PB. Test the leakae currentrelay
Thank you for sharing your project details, I appreciate it.
Thankyou!
Can you answer this question for me?
I live off of batteries (off-grid with solar and wind). I also experiment with direct connections of dc (no batteries, inverters, or charge controllers). Lately I’ve become interested in collecting my own hydrogen from the negative terminals of a large tank of water with two inlet holes. I came across your site and now I’m wondering about something. Hence, my question:
If a current can pass in a battery to create two gases (hydrogen and oxygen) or in my test tank (a 50 gallon tank), then why is the gases not being produced within the electric water heaters found within many homes?
I use direct current (electric water heater connected directly to a large solar array) and it acts like an on-demand water heater (of sorts)…it’s been working flawlessly for many years now…but suddenly I find myself with the DOH! feeling.
So my question of questions is, why isn’t my water heater a threat to my life? Where are those gases going? I would appreciate any constructive comments which can be emailed to me directly at kennyhendrick@protonmail.com
Thanks.
Thanks for asking this question.
Your water heater is not creating HHO gas in water because it is not passing current through water, it is passing heat through water. In order to generate HHO in water you will need to keep the positive and negative terminal of the DC supply immersed in water and at some distance apart, so that current across the terminals can traverse through water. Your heater is not doing this, instead it is immersing a heating coil inside the water which is causing heat to generate in water, it is not causing current to penetrate through water, and that is why no HHO is being generated.
DOH!
I’m old and stupid…sorry for that question Swagatam….I should absolutely have known that answer because I actually have several videos on the topic located at yandex zen and my own website!!!
The element within the tank!!!!!
And speaking of elements! If anybody wants to cook for free, simply connect any broken AC hotplate (after first removing all the superfluous ac junk that prematurely dies) and solder on two wires (it doesn’t even matter which way you connect those wires to the element either), now at the other end of those wires connect to a 48v solar panel (I have evolved beyond that. Nowadays I have 6 arrays of 48v in parallel to not only power my hot water tank and cook with (using several broken hotplates to create distilled water and other stuff), but also dump any residual to an mppt controller that keeps my batteries charged!
Thanks for that answer Swagatam (I was getting so worried for a minute there that I was about to flush the tank just to inspect it…phew).
No problem Kenny, I appreciate your honest feedback.
I grew up with asthma; I suffered sinus and respiratory infections my entire life. I started smoking at 16. When I was in my early 40s, my asthma was becoming increasingly worse. I was diagnosed with COPD at age 47. I am now 55. I quit smoking four years ago. The disease does not improve. My good days were far, i was scared that i wont survive it but i was so lucky to receive a herbal products from my step father who bought it while coming from South Africa for Rugby league, this herbal remedies saved me from this disease, at first it helps fight the symptoms of diseases and i was seeing good outcome, i had to use it for 13 weeks just as they Dr was prescribed and i was totally cure of asthma and COPD, (multivitamincare org ) do not hesitate to purchase from them they deliver across worldwide.
That is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate info… Thank you for sharing this one. A must read post!
Sir, The Oxygen produced by all the above methods will not fullfill the covid patients requirements as it ranges bet 2-6ltrs/minute.
Hello Suresh, I have only presented the concept of generating oxygen/hydrogen effectively using the cheapest possible method, I have never mentioned that this can be used for covid patients.
I don’t have 220v
I only have a solar panel
Hi Swagatam,
That’s great idea! Can we have quick chat? Please share your mobile.
Thanks
Shri
Hi. I havent read the whole blog but i was wondering that if you do isolate oxygen from this method, how are you going to store it? Thanks.
If I want to set up a plant for oxygen. Where I can get financed and machinery parts.
hi, do you know how to store oxygen separately from hydrogen? In this crisis, where medical oxygen is not available for Covid patients, can patients who require oxygen breathe in this stored oxygen?
The hydrogen being very light very escape into upper layers of the atmosphere…oxygen can be collected through bottle and tube arrangement, as we have in oxygen collecting apparatuses
a good concept and well known. but there are many things over looked here. As a chemical engineer I know some of the draw backs and how the set up is improved. there are many commercial electrolysers in market and you can make one for home use easily.
1) i can help anyone who is interested in making a sensible working unit for personal use.
2) the big risk is not electricty, AC or DC but the Hydrogen evolved. to is highly inflammable. DONT TRY THIS PROJECT INA CLOSED ROOM or ATHOME without understandingm. The hydrogen will explode.
Hello Swagatam,
Dear… in the wake of very short supply of Oxygen due to Corona… just for the help of needy… I want to start some basic oxygen making unit in the open… outside my society temporarily… I just want to know about the costs involved for making a four/ ten cylinder filling unit.. the space needed for it… if we fill for say 10 hours a day… how many cylinders will we be able to fill…
Lastly, can we get any monitoring help initially from your side… if you are putting up anywhere in and around Delhi…
Regards,
Sanjay
Hello Sanjay, the experiment shown above is very simple and effective, but collecting and storing the gases can be a tedious setup, and can be very costly. The concept shown in the first image looks good but will need to be implemented on a larger scale, however before going for the large scale, the setup must be tested on a smaller scale using the idea explained in the second last concept. The second last concept has the potentials of yielding the gases on a high quantity.
The above concept does not involve any complexity and will start the production as soon as power switched ON, except two things which are very crucial…the mains AC is dangerous and must be arranged with great caution, and oxygen must be collected carefully in cylinders with valves…and hydrogen must be allowed to escape in the air….oxygen and hydrogen should never be collected together in one cylinder which can cause explosion and fire…
I am situated in Mumbai, and mostly busy with my website work…
Thanks for your prompt reply Swagatam… Your work is giving hope to many people… Best wishes for future…
Regards,
Sanjay
Thank you Sanjay!!
Lastly… Can I put this blog address and your you tube video in my you tube video for the purpose… I will give due credits of course… and even the blog/ video link will lead directly to your place…
Regards,
Sanjay
OK, It will do, no problem!
the best is to make a portable system that has a tight pipe to take H2 out of the house or keep the appliance out of the house and have a pipe coming into the house which has 02 for covid patients. As a per my calculation a unit to support one person can be economically built. Major costs is graphite electrode and bride rectifier. Compressing O2 and transporting it is much bigger problem and there is shortage of cylinders and also regulators
Sir
How we will collect the oxygen????
Please see the first image, you will have to connect tubes or cylinders with valves to collect the gases.
Hi if I use a car battery and jumper cables with large wire mesh will this work to complete electrolysis I want to have 20% dissolved O2 in my water. If I were to use this in a 35gallon trash can would that create to much hydrogen for safety?
Hi, I am not sure about it, it may be quite difficult to guess the results of the experiment in terms of hydrogen production, but the electrolysis process will happen for sure, provided the mesh electrodes are within an inch distance
So I need two wire mesh grates 1inch apart not connected and way except for the water. Otherwise one grate positive one grate negative? But because I’m using a car battery I can have a larger metal grate.
Yes that’s right, no matter how the mesh is arranged, the +/- terminals need to be 1 inch apart or even lower.
Cool appreciate the reply.
Thank you a lot for these DIY instructions. It is truly amazing no one else posted such an easy to understand setup for water electrolysis.
It is important that the water be pure, without any contaminants, which could interfere with H and O to form unwanted compounds. The easiest way to pure the water is by distillation: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distilled_water
Btw, I think you can actually produce water out of HHO from electrolysis process very easily. Just join the outputs of your gas tubes into a common container and you should see water forming there as a result. Which is kinda expected as you also noted the reason why the AC won’t work and DC is required.
Thank you again for these GREAT instructions! Really appreciated.
Thank you for liking the post, appreciate it very much.
Distilled water is actually not required, tap water is just enough, the slight impurity it has might not create any serious problems with the HHO gas production. However, it would be interesting to see how distilled water would react to the 310 V DC input.
Pure distilled water is not conductor. This mean you can not make electrolysis with pure distilled water.
It can be done with brute force through a high 300 Dc
Hello Swagatam
This is Dr Harshit from Mumbai.
I need your help urgently to help corona patients who require oxygen
Thank you so much.
Hello Doctor Harshit, The project will require significant amount funding, if you have the necessary arrangement then hopefully we can proceed. I will email you for the required details.
Hi Swagatam, could you please send me the details as well for required funding? Thanks!
Thanks AJ, the set up might require extensive external hardware which cannot be developed quickly, will need a lot of planning and designing for getting the desired results
Sorry, One More point…
As far as oxygen is concerned… I would be doing it more for charity but What about the Hydrogen we collect… is it of any use, anywhere…
Hydrogen gas is an extremely useful fuel, but managing the gas cautiously is difficult, since it is too inflammable.
Thank you for sharing this useful information. I am working on producing huge amount of oxygen for commercial purposes, from my previous readings I have found out that production of oxygen in large scale for commercial purpose is unprofitable because of the very high electrical energy required.
What’s your view about that?
I appreciate your feedback, in that case you can probably try using a solar panel or windmill for getting cheap electricity.
Thank you I may consider that..
Thank you for this. I have been considering making one though I still need to do some research. I am a former submariner, and this is how we made oxygen while underway. I suffer from asthma occasionally and on days like this week and a half, breathing is at a premium. I know on the boat we had to worry about o2% levels too high we could explode, too low, we stopped breathing, basically falling asleep and never waking up. I like waking up and not exploding.
Sounds interesting, you can probably regulate or control the oxygen production rate by selecting the electrode size appropriately, since its surface area determines the rate of production….other factors like voltage, distance between the electrodes etc also affect the rate of oxygen production
we did it in the Chemistry lab at uni.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrolysis_of_water they mention using a small gap to keep the current/voltage requirements low
it’s a standard scientific method to electrolyse pure water
btw unless you use fully de-ionised or reverse=osmosis water you will get toxic gases comign off with the H and O so be very careful what you do.
in addition you have 220v with a higly explosive mix of hydrogen and oxygen – this is why it’s not openly discussed by amateurs online, do it enough and you will make a tiny mistake and blow up your house. (we use fume/extractpr hoods to capture any gasses we didn’t collect in the tubes – I’ve forgotten the formulas now but you can simply work out exactly how much gas for the number of Amps used)
Can water be electrified in a vacuum using high voltage jump spark so that electrodes won’t be touching water
Hello sir,
With this method, how many hours or days will it takes to convert a gallon of water to HHO, it doesn’t have you be accurate sir.
I will be very happy
Hello Lawal, it will depend on the surface area of the electrodes, so try to make the surface area of the electrodes as large as possible, and speed up the process to the maximum possible levels…
OLA SWAGATAM SOU DO BRASIL, ME INTERESSEI MUITO POR ESTE CIRCUITO DE DIODOS PARA USAR EM CELULA DE HHO, EU OBTIVE UMA TENSÃO DE 108 VOLTS DC,EU TE PERGUNTO SE EXISTE PWM QUE POSSA CONTROLAR ESTA ESTA VOLTAGEM, E SEU PODERIA USAR ESTE SISTEMA EM CELULA DE HHO DE PLACAS DE AÇO INOX DE 1 MM DE ESPESSURA….? OBRIGADO PELA SUA ATENÇÃO E PARABENS PELO SEUS PROJETOS E INVENTOS É DE GRANDE IMPORTANCIA PARA TODA A HUMANIDADE OBRIGADO NOVAMENTE.
Graças Wallace, você pode tentar um dimmer de luz ou qualquer dimmer de ventilador de teto ordinário e usá-lo para controlar o nível HHO ….
Super like
Really thanks for sharing this idea…
Is there anyway we can monitor the volume of gases evolved? This is important in order to use this fuel cell in practical applications.
It could be probably done using the following explained gas sensor module and by configuring its output with a digital voltmeter
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/2015/04/gas-leakage-alarm-circuit.html
electrolysis at reduced voltage will be highly inefficient and ineffective, unless an external agent is added which would result in generating some other gas instead of HHO
by the 220V is not dangerous until it's handled with negligence and ignorance.
thanks, but please do not misinterpret something wrongly, here's what's written in the above article:
THIS METHOD HAS BEEN DISCOVERED BY ME, I ASSUME SO, BECAUSE IT'S NOT BEEN DISCUSSED ANYWHERE ELSE ON THE NET SO FAR.
here the "method" refers to the using of 220V DC for the electrolysis and absolutely without any external chemical such as salt of soda.
show me one link on internet which has explained this process.
Hydrogen released in this process is twice the amount of oxygen. so the flask containing negative electrode will have more amount of hydrogen and more pressure. This pressure will push down the water in the inverted falsk.
So the whole system has to be contained effectively using valves and pressure guages.
thank you for the info…!
You might be right or wrong. It is fact that you will get two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen from one molecule of water. This doesn’t mean that 2 atoms of hydrogen are two times bigger (in volume) than 1 atom of oxygen (by the way oxygen always appear as O2 – two atoms of oxygen are connected together). Maybe some chemistry engineer can say if your statement is true or not.
hi swagatam i tried this method but i dont know whether it is releasing oxygen nd hydrogen am using graphite rods which are taken from batteries and are placed in 20ml syringes and gas is coollected by connecting the syringe to a pipe… but am not observing any reduction in water in positive electrode after some time the water becomes yellowish colour pls help me its urgent i shud cmplete my project
Hi power star,
since water is made up of H2O, then obviously the process is going to generate HHO in the relevant chambers, but do not use any form of catalyst like baking soda or salt…because simply it's not required.
the yellowish color could be due to impurities in water.
single graphite rods will not yield anything significant and could take days and months for the water to get reduced and converted to HHO…..you will need arrays of such electrodes or square graphite plates arranged in stacks in 2mm gap in order to get maximum response in minimum amount of time.
Oo thanku.. instead of plates any other??
try to use electrodes with maximum surface area in the water
Thanks for providing this information!!
using this system what is the amps, also what is the volume of gases generated.
I did not measure these parameters.
Wow I want someone to teach and mentor me about chemistry and physics
As a matter of interest regarding my question about pressure/H2O etc – a wikipedia page that speaks about 'Nernst equation' & 'cold fusion' says
"… calculated that a palladium cathode immersed in a heavy water electrolysis cell could achieve up to 10 to the 27 atmospheres of pressure on the surface of the cathode, enough pressure to cause spontaneous nuclear fusion. In reality, only 10,000-20,000 atmospheres were achieved."
Although not an answer to my simple question, I am reminded that 'If you sup with the Devil. Use a long spoon.' 🙂
Thanks for the info Steve, and make sure the spoon is long enough 😀
ok – thanks Swagatam. As you suggest others my be able to comment.
Helo again Swagatam,
Thank you for your kind reply. You have set me thinking about the following:
If two carbon rods where set into the walls of a very high pressure (non conductive) container that was completley filled with clean water then hydrolysis started. Would you care to speculate on what order of pressuere would eventualy build up in the tank as the H2O was split?
Hello Steve, that sounds very interesting, however being exclusively from the electronics domain, I have very little idea regarding how chemical reactions work, so I may not be the right person to speculate this, may be some other knowledgeable gentleman would want to comment on this.
That's an INCORRECT information.
HHO from electrolysis process can never form Dihydrogen monoxide or water.
By the way Dihydrogen monoxide is just an alternate scientific name for water.
Please do not encourage Hoax, and stay away from deceptive and malicious information
Hi Swagatam.
You leave a comment for me that says:
Please do not encourage Hoax, and stay away from deceptive and malicious information
I'm sorry you think any of the information I gave was a Hoax, deceptive or malicious information.
As I said "I am only a Layman, but I do believe"(Please note is said 'believe'), and I did not say that (I know!), and I still do 'believe' it to be the truth that:
1)If you mix Pure Oxygen and Pure Hydrogen you may get water / 'Dihydrogen Monoxide'.
2)Graphite rods which are taken from batteries may contain noxious chemicals and dangerous metals, you would probably be better off with the graphite Rods that you buy four pencils.
3)Note: "pencil leads" do not have lead in them, they are made from graphite and clay.
4)Even though the size of "pencil leads" is small, a few fix together will give you a greater surface area then one large rod.
5)The "Facts About Dihydrogen Monoxide" Was just a bit of fun information and Light reading for your followers.
I did notice that one of your readers was thinking about making oxygen to breathe so I do think that point two three and four are very valid points in this case.
I have looked at many of your circuits, and I have seen how hard you have worked to help people, in my mind you are a great person, and you seem to have a great knowledge electronics.
I would just like to say thank you for your articles, and thank you for making the world a better place.
I do not know which post or where in my posts there was deceptive or malicious information, so I'm going to delete all my comments, feel free to repost any of my points that you may think applicable accurate or necessary.
So sorry for bad post, wish you all the best for you and your site.
Regards, Lee
Thank you Lee for clarifying your point of view, I did not mean to hurt you, I was just worried about the fact that readers might get a wrong impression about the above circuit, and get confused whether to use it or not.
I strongly believe that HH and O in the atmosphere can never combine until these are forcibly fitted through some specialized equipment.
Anyway, I appreciate your concern and sensibility…please keep reading my articles and feel free to express your thoughts through your valuable comments.
Hello there to everyone of you. Congrats to Swagatham who has covered many diverse but connected fields in electronics such as the H2O2 gas generators here . As someone who has dabbled in the above field for a very very long time I wish to make some imp and personally experienced
observations regarding the diff aspects of splitting/recombing of Hydrogen and oxygen back into water. Some have made similar small variations of combined gas called HHo lot more popularly known as ‘Browns gas’ which is nothing but Hydrogen& Oxygen that was liberated from the water which is collected off a single “outlet” and passed through a water chamber to prevent “flashback” that could easily occur for a variety of reasons in order to prevent a nasty explosion. This Hho is then escorted into the fuel inlet of(modified)! Int Combustion Engines that have given a very good account of themselves which you may have seen/heard of ‘vehicles running on water’ , but the idea hasn’t really taken off as work on that aspect is usually never really “over” so to speak. That gas which is used for powering the ICE is truly a great gift if I may say so because compared to the myriad varieties of toxic combinations of emissions that come out of a gasolene powered vehicle, the output that comes out of a water powered vehicle is basically only water itself compared to the pollution coming from a regular ICE. That’s it. Now this in my opinion is a very attractive way of generating water from Hydrogen and Oxygen as some readers wanted. You get the additional benefit of mechanical energy also along with that. One imp reason why research is still going on in this aspect and why this tech is not embraced by the community at two or three basic problems. Even after using a noble form of aluminium (Other materials don’t tick) used as separators in the fuel cell, these separators tend to accumulate nasty sludge/muck that starts to diminish the pwr Opt of the said cell/s. Another problem is that the valves in the engines start getting pitted which obviously leads to other engine complications. Another obvious outcome was the engine temp that used to rise significantly. motorists who ride on lpg will obviously notice this as much more than ‘usual’. Finally I must stress that considering the dramatic interest by many people about this, more esp beginners, no amount of warning is really enough about the lethal aspects in meddling with the ‘Devil’ himself so to speak. The inflammability of Hydrogen Vs ANY other fuel is much much worse than comparing your kitchen gas and petrol, (I’m sure you’ve heard ABT the Hydrogen bomb). And the speed of migration of (ignition factor) hydrogen is really phenomenal. I suggest intensely that everyone, esp newcomers not to involve themselves unless they have covered all aspects in this connection. Have a nice day, take care. Bye
Thank you Prashanth, for the valuable information, I hope the readers will find it very useful…
And I am very glad you liked my articles, it's a great pleasure to have readers like you in my website
Hello Swagatam Your process is similar to stanley myer electrolysis by using high voltage and high frequency power source and best to be resonant frequency of water moleculer that cause breaking hydorgen bonds ..but the above method it think it is generating HO gas and not pure Oxygen .. So can you confirm if it is generating pure Oxygen
Best regards
Hello Ossama, since water is composed of hydrogen also we cannot stop its generation. Moreover in electrolysis hydrogen will be generated along with oxygen. However here, since the two electrodes are separated by a good distance and Hydrogen being much lighter will quickly escape through the home ventilation, leaving behind pure oxygen. To make it even more safer, we can terminate the hydrogen gas through a pipe system outside the premise.
Hello Swagatam,
I have to realy admire your patience in dealing with most of the comments addressed to you about making gasses this way. I I have been working in electronics & electrics for over 60 years. I would NEVER have the courage to present such a high(ish) voltage method to 'lay' people. Please discourage your readers from using 'table salt' + low voltage as this will make chlorine also. If they try 'salt' with your circuit (nothing wrong with it as you have well advised) then they will be in for very bad news. Also stress the use of carbon electrodes (unless you have some platinum about!) & insulate any copper used to connect to them that is under water or they will be introduced to eletroplating (Areldite epoxy glue is good.) Keep up the good work & thanks.
Steve Bloggs
Thanks so much Steve,
I am aware of the dangers associated with the above design and that's why I have put the warning message at the bottom of the article. I have also suggested the elimination of any kind of external chemical agent in the procedure which would actually spoil the purpose of the proposed experiment.
In one of the comments I have also recommended the use of graphite rods instead of metal…
Anyway, I appreciate your valuable concern and hope that the viewers read and understand the precautions emphasized by you.
Many thanks.
hi swagatam,
you said via AC you will get force so that gases will get separate but y again you are converting AC to DC via rectifier,then it is as usual rite i.e, it will get power from DC only rite
Hi power star,
it's the voltage level that's important, and AC will never work actually.
therefore the AC is rectified to DC at around 300V, which makes it possible to force the electrolysis significantly even without an external catalyst agent.
So the Diode are converting AC to DC and then node get electrolized which break H2O molecules and separates Oxygen out, hopefully if we can store this like each house definitely has cooking cylinder empty, if can be cleaned and stored within and this can be circulated among at least a society level which helps humanity in this crisis at least. Make in India Concept
You have understood it correctly, but storing it in airtight containers is something which may be extremely difficult to implement for a common man.
hi,
I have been suffering with heart problem, it cause low oxygen levels in my body, could you please tell me can I use this experiment for making oxygen for increase body oxygen. kindly give me the details. I am poor I cannot purchase oxygen concentrate machine. please contact me at rcheburthy@gmail.com. thank you.
The above set up will generate oxygen and hydrogen for sure, hydrogen will go up in the air since it's lighter than air, oxygen will stay in the premise, however I am not sure whether it will hep your cause or not, you better consult a physician about it.
Use graphite material for the electrodes.