An infrared flood light is a circuit that creates an illumination over a wide range of area using infrared frequency. This infrared illuminated area can be perfectly visualized through specialized infrared gasses and IR cameras, but can be totally invisible to naked eye.
In this post we study a simple infra red based flood light system which can used for illuminating large landscapes during night for monitoring wide aresa through IR spectacle.
The Design
The adjoining design shows a simple IR flood light circuit diagram for IR illumination applications.The 4049 section is the basic voltage doubler circuit which effectively boosts the 9 V supply to a level of around 15 V which further becomes the supply voltage for the next 555 pulse modulator section.
The voltage is suitably pulsed as per the settings of P1 and P2 for driving the associated IR LEDs.
The main feature of this infrared IR LED flood light circuit is that it utilizes just a single PP3 9 volt battery and yet is able to provide lights (IR) at dazzling levels.
Infra Red (IR) LED Flood Light Circuit Diagram
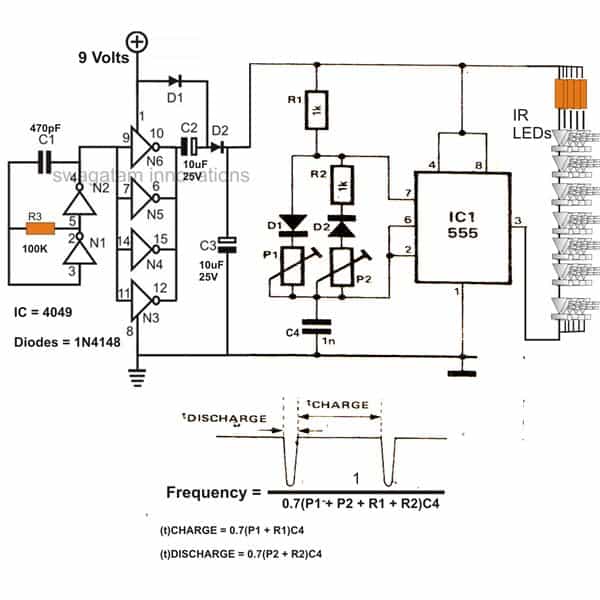
Parts List
- Resistors are 1/4 watt 5% CFR
- 100 k = 1
- 50 Ω = one on each LED string
- 1 kΩ = 2
- P1, P2 preset trimpots 10 kΩ = 2
- Capacitors
- Ceramic 470 pF = 1
- Ceramic 1 nF = 1
- Electrolytic 10 µF / 25 V = 2
- Semiconductors
- Diodes 1N4148 = 4
- IC 555 = 1
- IC 4049 = 1
- Infrared LEDs = as per the requirement on the LED strings
How to Calculate the Components
Oscillation Frequency of the 555 Timer (Astable Mode):
The 555 timer operates in astable mode, generating a pulsed output for driving the IR LEDs. The frequency of oscillation is given by:
f = 1 / [0.7 * (P1 + P2 + R1 + R2) * C4]- P1 and P2: Potentiometers (used for adjusting charge and discharge times)
- R1 and R2: Fixed resistors
- C4: Timing capacitor
Charge Time (tcharge):
The charge time is determined by the resistors P1 + R1 and the capacitor C4:
tcharge = 0.7 * (P1 + R1) * C4Discharge Time (tdischarge):
The discharge time is determined by P2 + R2 and C4:
tdischarge = 0.7 * (P2 + R2) * C4Total Period (T):
The total period of the oscillation is the sum of the charge and discharge times:
T = tcharge + tdischarge
T = 0.7 * [(P1 + R1) + (P2 + R2)] * C4Frequency (f):
The frequency of oscillation is the reciprocal of the total period:
f = 1 / T
f = 1 / [0.7 * (P1 + P2 + R1 + R2) * C4]Example Calculation:
Lets Assume the following component values:
P1 = 10 kΩ
P2 = 10 kΩ
R1 = 1 kΩ
R2 = 1 kΩ
C4 = 1 µF
Step 1: Total Resistance in the Timing Network:
P1 + P2 + R1 + R2 = 10 k + 10 k + 1 k + 1 k = 22 kΩStep 2: Calculate the Frequency:
f = 1 / [0.7 * 22 * 103 * 1 * 10-6]
= 1 / [0.7 * 22 * 10-3]
≈ 1 / 0.0154 ≈ 65 Hz
f ≈ 65 HzIR LED Driver Section:
The IR LEDs are driven by the output of the 555 timer which pulses them at the calculated frequency. The current through the LEDs depends on the supply voltage (9V) and the series resistors. The diodes (D1 D2) and capacitor (C3) help stabilize the supply voltage and reduce noise.
Resistor Selection for LED Current Limiting:
Use Ohms Law:
RLED = (Vsupply - VLED) / ILED
Let us assume Vsupply = 9 V, VLED = 1.5 V (for IR LEDs), and desired ILED = 20 mA.
RLED = (9 - 1.5) / 0.02
RLED = 7.5 / 0.02
RLED = 375 ΩWe can Use a standard resistor value of 390 Ω.