In this post we see how to build an enhanced and efficient car headlight lamp using Pirhana LEDs.
A car LED headlight is a powerful lamp built using high efficiency LED arrays, which creates extremely powerful headlight lamp for the car, along with a very high efficiency in terms power consumption.
Using 4-pin Pirhana LEDs
You might be pretty familiar with the ordinary two-pin, 5mm white LEDs, which are by no means “ordinary” and produce lights at reasonably high intensities.
However when it comes to 4-pin LEDs, the 2-pin types stand no where near it. Include just 50 of them in a group, and you are well producing lights that may be more dazzling than conventional car headlight intensities.
Here I have explained how to implement 4-pin LEDs in automobiles for making their headlights more power efficient and more powerful.
In fact the application may not be restricted to just car headlights, you might want to use them for other applications also, like as a LED tube light in your home, that can result in a lot of saving in your electrical utility bills.
Before we proceed with the proposed circuit of efficient high power LED head light design details, let’s first analyze the important specs of this interesting light emitting device.
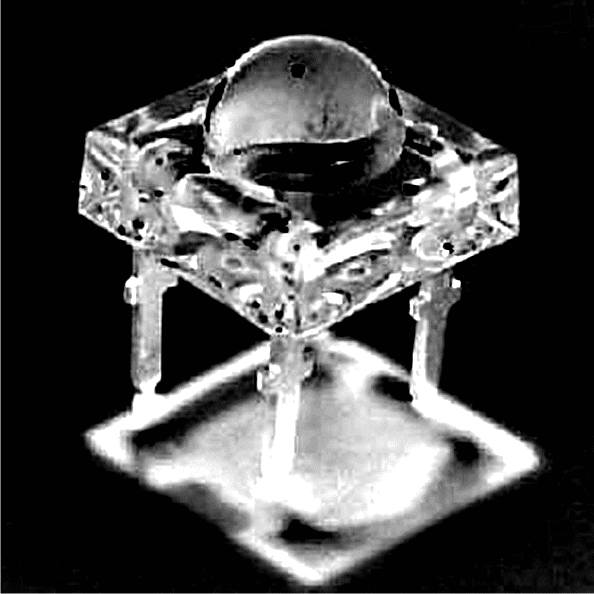
A 4-pin super bright piranha LED might look complex at the first appearance, but a careful look will assure you that it’s as easy to understand as a two pin type.
Though the device includes 4 pin outs, two on each side are actually shorted internally, and therefore technically it has just two outputs, one anode and the other cathode quite like our ordinary two pin LEDs.
However a four pin arrangement is made to suit it’s size and for assisting firm PCB mounting, the square extra large shape of a 4-pin LED is designed to introduce some special features in it, attributing the qualities of generating extravagant light emissions to them.
Main Specifications of 4-pin super flux LED
The following text provides some of the important specs related to 4-pin LEDs:
- Safe operating temperature – 25 to 80degree Celsius
- Typical operating voltage – 3.5 volts,
- Maximum operating voltage – not to exceed 4 volts.
- Normal continuous operating current – 20 mA,
- Peak instantaneous current – up to 100 mA Viewing angle – 50 degrees.
Efficient Car Headlights Using 4-Pin Super Flux Piranha LEDs
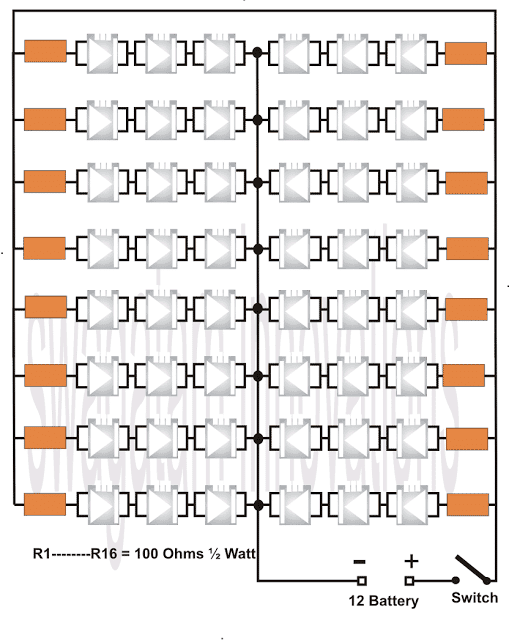
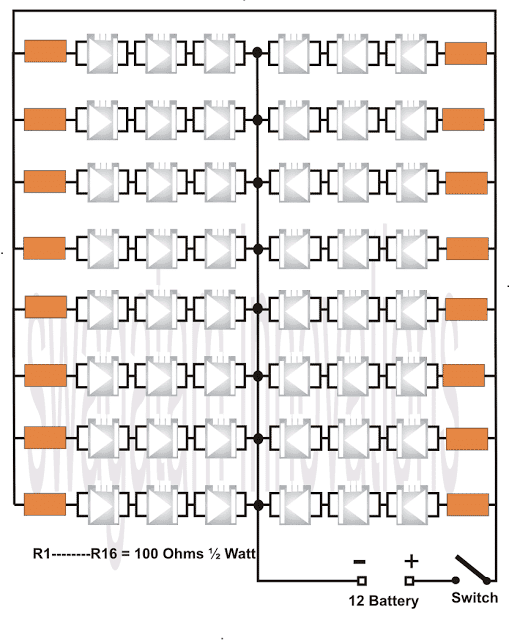
The DIAGRAM illustrates a simple application circuit using 48 high intensity 4-pin LEDs for automobile headlights.
Since the operating forward voltage of the LED type is around 3.5, three of them accommodates in each channel, in series.
The series are further connected in parallel for making the total number up to 48. Voltage is derived from the car battery via the dashboard switch.
Preferably the LEDs may be arranged in circles for uniform distribution of light across the whole headlight enclosure.
Circuit Diagram
The PCB used must be a glass epoxy type, double sided; the hind side copper of the laminate is not etched and is used as a heatsink for absorbing heat from the LEDs and dissipating it in the air.
Using a Single 10 watt LED
If you thing the above discussed method is too laborious, then you can opt for a single 10 watt LED for enhancing your car headlights with low consumption LED lights.
The following image shows how a 10 watt LED actually looks like:
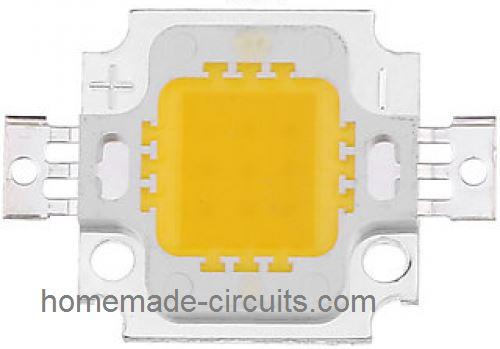
The two fins across the sides are the two terminals which will connect with the 12V supply from the car.
Not to mention each of these LEDs on the headlights must incorporate a current control circuit in order to ensure a safe and an optimal illumination, as shown below.
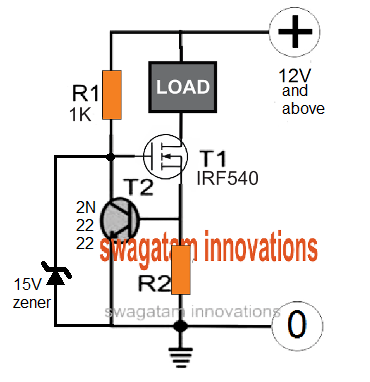
R2 is the current sensing resistor and could be calculated as discussed in the below sections.
I have already posted a couple of LED current limiter circuits which you can study through the following links, and implement those in between the LED lamp and the 2V supply from the battery:
Current Limiter using Transistors
Any of the above concepts can be applied for protecting the 10 watt car headlight LED lamps from over current or a thermal runaway situation.
However make sure the LEDs are mounted over well calculated heatsink, which could be a round finned type as shown below, this may be mounted behind the headlight box:

Using other Forms of LEDs
If you wish to use any other form of LED having different specification than the above, you can definitely do that by calculating the resistor values appropriately by using the formula:
Resistor = Supply voltage - Total Forward V spec of the LED series / LED current
R = (Vsupply - Vf) / ILED
Where:
- R = Current Limiter Resistor value
- Vsupply = Supply voltage
- Vf = Total Forward Voltage specification of the LED series
- ILED = Maximum Safe LED current
For example suppose you would want to make a headlight lamp using 1 watt, 3.3V 350mA LEDs, and your supply voltage is 12V from your car battery, in that case the above formula could be calculated in the following manner:
Consider each string has 3 LEDs in series:
R = 12 - (3.3 x 3) / 0.35 = 6 Ohm
o it is 6 ohms resistor that you would need to put in series with each of the LED strings having 3 LEDs in series.
And what about the resistor wattage or the power?
For evaluating wattage simply multiply the difference between the supply and LED total voltage drop with the LEd current, therefore for the above case we get:
Power = 12 - (3.3 x 3) x 0.35 = 3.46 watts, the nearest safer value is 4 watts.
In this way you can use any desired LED for your car headlight by suitably calculating the series current limiting resistor.
Adding a PWM Intensity Control
One added advantage of a LED based car headlight is that it can be facilitated with a PWM intensity control, which will not only enable the user to vary the intensity of the car headlight as desired, but also save precious battery power.
The following image shows a simple IC 555 PWM control that can be used for the mentioned purpose very easily and effectively.
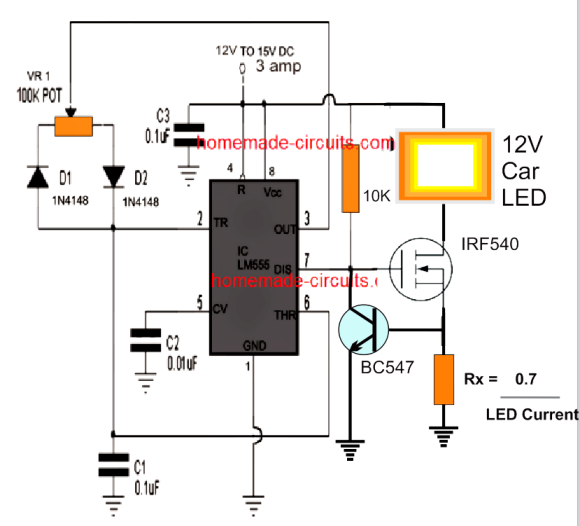
The above design also features a current controller stage which ensures that the LED can never consume more that the rated current and thus work safely under all circumstances. The resistor Rx must be appropriately calculated depending on the maximum current rating of the LED.
The MOSFET must be mounted on a suitable heatsink to ensure optimal performance from the LED.
Caution: When high wattage LEDs are used always make sure to add a specialized current limiter stage in between the supply input and the LED module, as already explained in the previous paragraphs of this articles.