In this post I have explained the making of simple delay timers using very ordinary components like transistors, capacitors and diodes. All these circuits will produce delay ON or delay OFF time intervals at the output for a predetermined period, from a few seconds to many minutes. All the designs are fully adjustable.
Importance of Delay Timers
In many electronic circuit applications a delay of a few seconds or minutes becomes a crucial requirement for ensuring correct operation of the circuit. Without the specified delay the circuit could malfunction or even get damaged.
Let's analyze the various configurations in details.
You may also want to read about IC 555 based delay timers. Recommended for you!
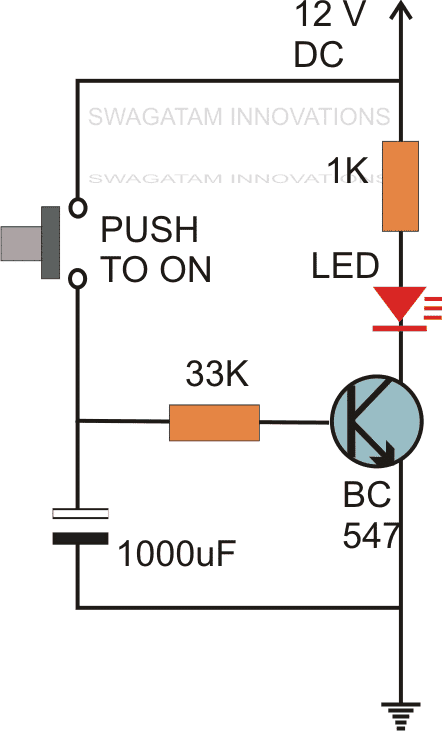
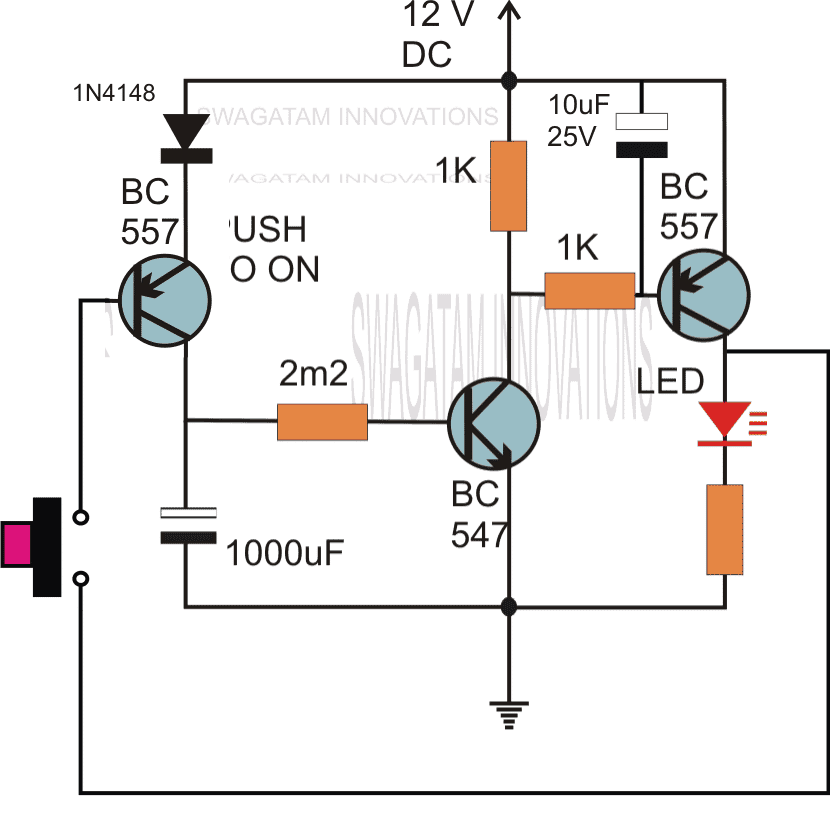
Using a Single Transistor and Push Button
The first circuit diagram shows how a transistors and a few other passive components may be connected for acquiring the intended delay timing outputs.
The transistor has been provided with the usual base resistor for the current limiting functions.
A LED which is used here just indication purposes behaves like the collector load of the circuit.
A capacitor, which is the crucial part of the circuit gets the specific position in the circuit, we can see that it's been placed at the other end of the base resistor and not directly to the base of the transistor.
A push button is used to initiate the circuit.
On depressing the button momentarily, a positive voltage from the supply line enters the base resistor and switches ON the transistor and subsequently the LED.
However in the course of the above action, the capacitor also gets charged fully.
On releasing the push button, though the power to the base gets disconnected, the transistor continues to conduct with the aid of the stored energy in the capacitor which now starts discharging its stored charge via the transistor.
The LED also stays switched ON until the capacitor gets fully discharged.
Te value of the capacitor determines the time delay or for how long the transistor stays in the conducting mode.
Along with the capacitor, the value of the base resistor also plays an important role in determining the timing for which the transistor remains switched ON after the push button is released.
However the circuit using just one transistor will be able to produce time delays which may range only for a few seconds.
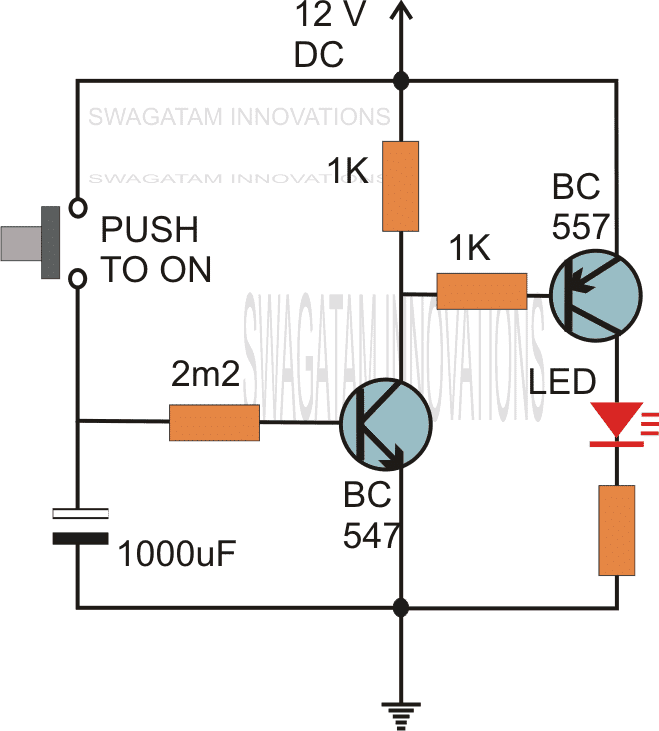
By adding one more transistor stage (next figure) the above time delay range can be increased significantly.
The addition of another transistor stage increases the sensitivity of the circuit, which enables the use of larger values of the timing resistor thereby enhancing the time delay range of the circuit.

PCB Design
Video Demonstration
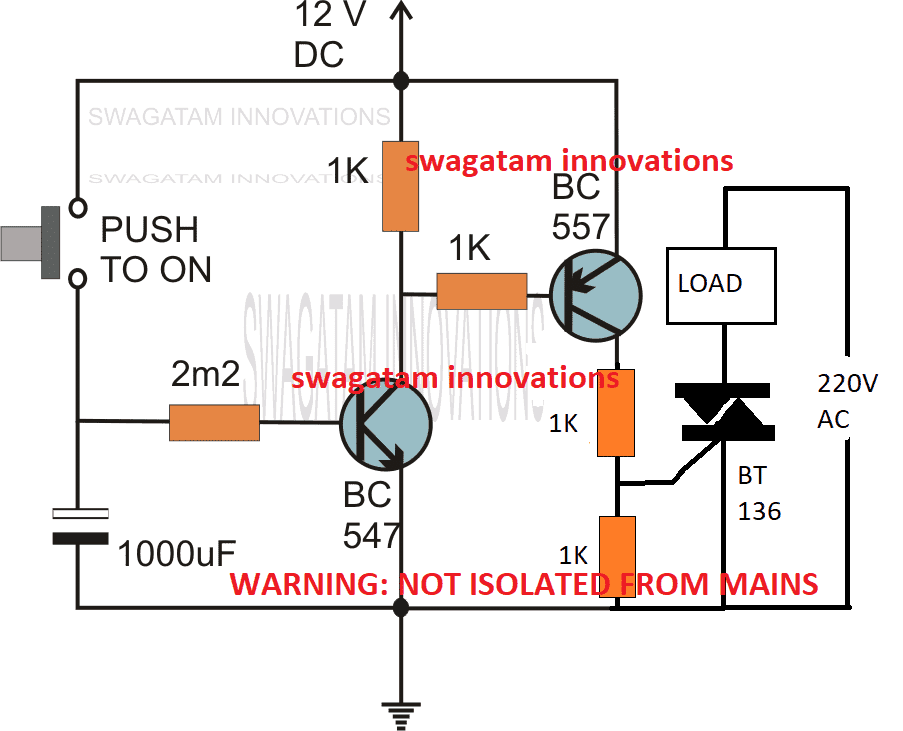
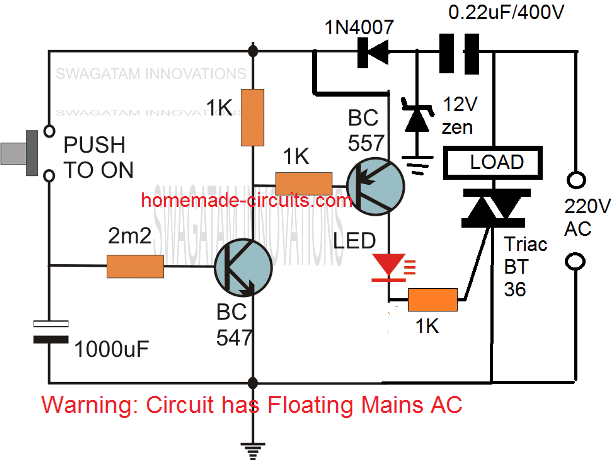
Using a Triac:
The following image shows how the above delay timer circuit may be integrated with a triac and used for toggling a mains AC operated load
The above could be further modified with a self contained power transformerless power supply as shown below:
Without a Push-Button
If the above design is intended to be used without a push button, the same may be implemented as indicated in the following diagram:
The above delay OFF effect without a push button can be further improved by using two NPN transistor, and by using the capacitor across base/ground of the left NPN
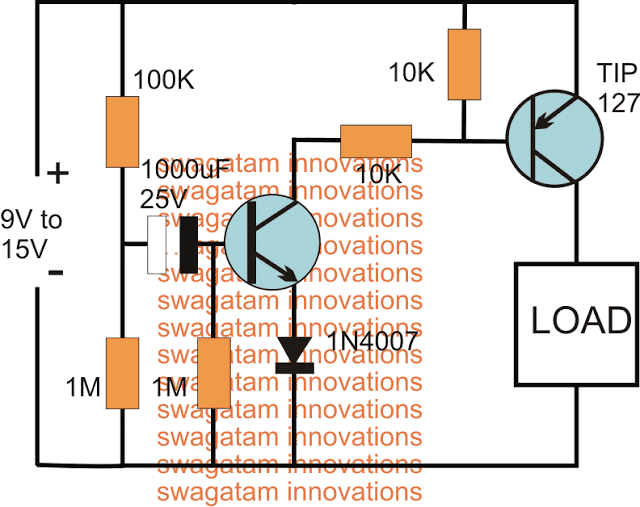
The following circuit shows how the associated push button may be rendered inactive as soon as it's pressed and while the delay timer is in the activated state.
During this time any further pressing of the push button has no impact on the timer as long as the output is active or until the timer has finished its delay operation.
Delay from an External Trigger
Problem asked by Mr. Glen (one of the dedicated readers of this blog):
I have a situation where I have a pulse of 12V that lasts about 4 seconds (from a rotary switch being turned by a slow motor) but I only want about half a second pulse (to trigger a mechanical bell/chime).
Is there any way to take a long pulse into a circuit and send a much shorter pulse out?
The solution to the above problem is provided in the following schematic:
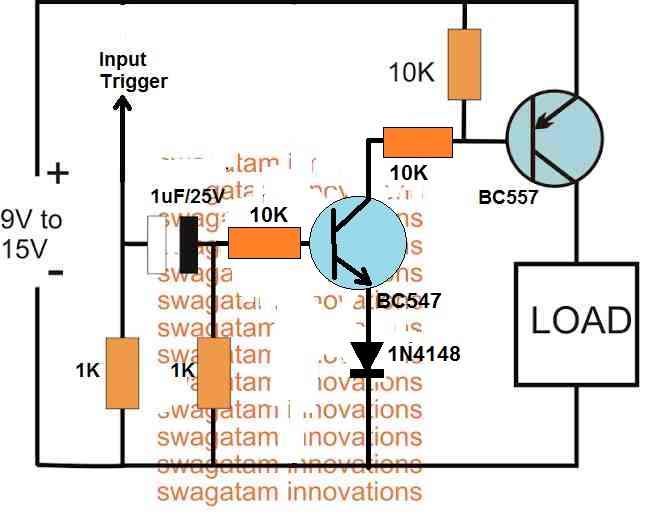
Two Step Sequential Timer
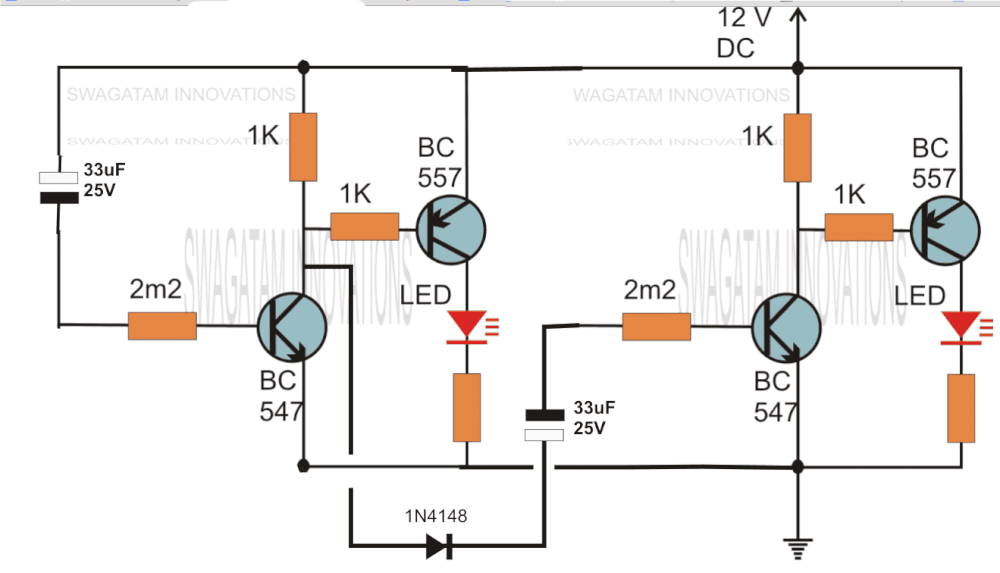
The above circuit can be modified to produce a two step sequential delay generator. This circuit was requested by one of the avid readers of this blog, Mr.Marco.
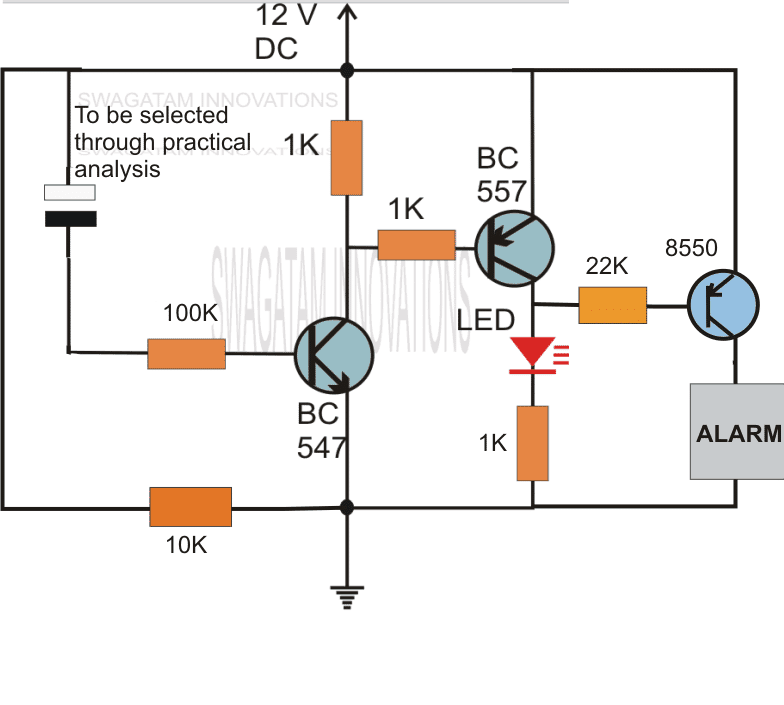
A simple delay OFF alarm circuit is shown in the following diagram.
The circuit was requested by Dmats.
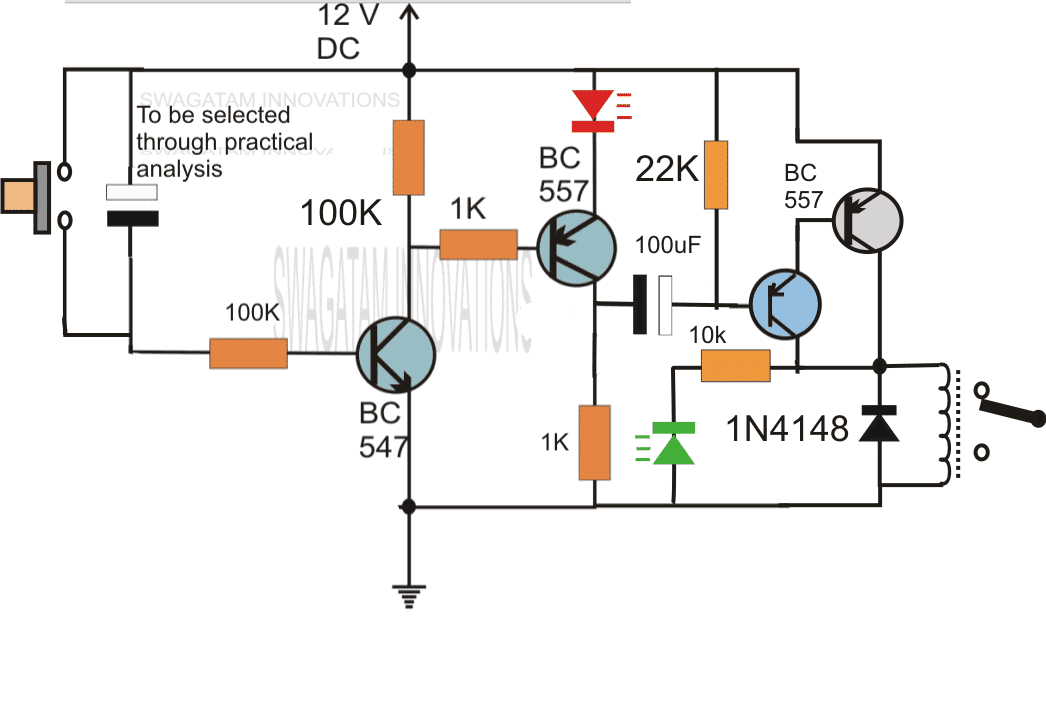
The following circuit was requested by Fastshack3
Delay Timer with Relay
"I am looking to build a circuit that would control an output relay. This would be done in 12V and the sequence will be initiated by a manual switch.
I will need an adjustable time delay (possibly displayed time) after the switch is released, then the output would go on for an adjustable time (also possibly displayed) before shutting off.
The sequence would not restart until the button was pressed and released again.
The time after the button release would be from 250 milliseconds to 5 seconds. The "on" time for the output to turn on the relay would be from 500 milliseconds to 30 seconds. Let me know if you can offer any insight. Thanks!"
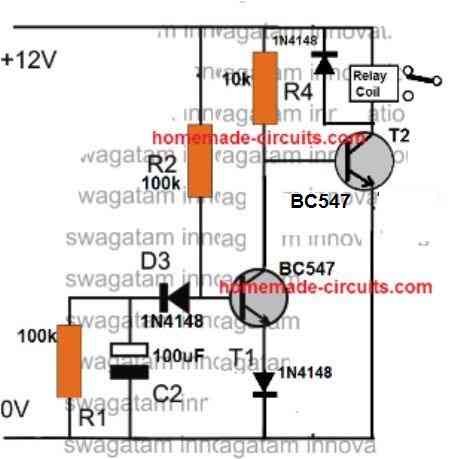
So far we have learned how to make simple delay OFF timers now let us see how we can build a simple delay ON timer circuit which allows the connected load at the output to be switched ON with some predetermined delay after power switch ON.
The explained circuit can be used for all applications which calls for an initial delay ON feature for the connected load after the mains power is switched ON.
Delay ON Timer Circuit Working Details
The shown diagram is pretty straightforward yet provides the necessary actions very impressively, moreover the delay period is variable making the set up extremely useful for the proposed applications.
The functioning can be understood with the following points:
Assuming the load which requires the delay ON action being connected across the relay contacts, when power is switched ON, the 12V DC passes via R2 but is unable to reach the base of T1 because initially, C2 acts as a short across ground.
The voltage thus passes through R2, gets dropped to relevant limits and starts charging C2.
Once C2 charges up to a level which develops a potential of 0.3 to 0.6V (+ zener voltage) at the base of T1, T1 is instantly switched ON, toggling T2, and the relay subsequently....finally the load gets switched ON too.
The above process induces the required delay for switching ON the load.
The delay period may be set by appropriately selecting the values of R2 and C2.
R1 ensures that C2 quickly discharges through it so that the circuit attains the stand by position as soon as possible.
D3 blocks the charge from reaching the base of T1.
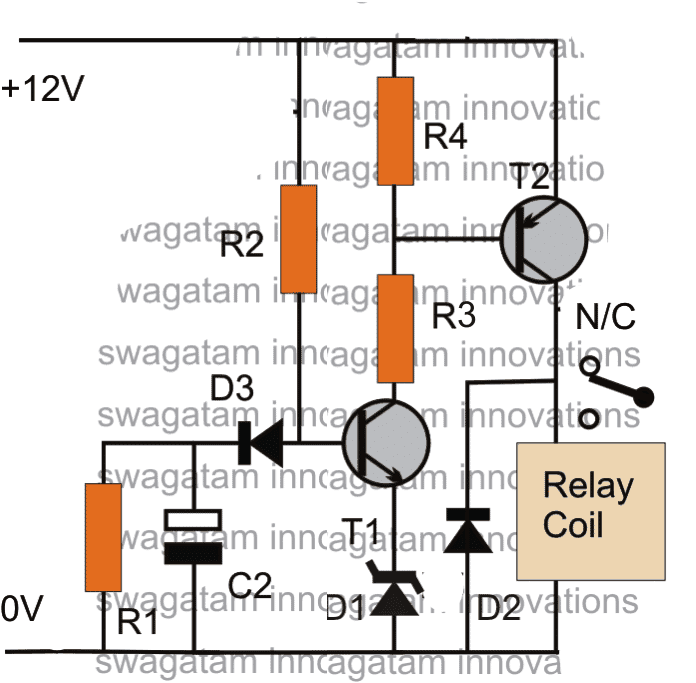
Parts List
R1 = 100K (Resistor for Discharging C2 when circuit is switched OFF))
R2 = 330K (Timing Resistor)
R3= 10K
R4 = 10K
D1 = 3V zener diode (Optional, could be replaced with a wire link)
D2 = 1N4007
D3 = 1N4148
T1 = BC547
T2 = BC557
C2 = 33uF/25V (Timing Capacitor)
Relay = SPDT, 12V/400 Ohms
PCB Design
Application Note
I have explained how the above delay ON timer circuit becomes applicable for solving the following presented issue by one of the keen followers of this blog, Mr. Nishant.
Circuit Problem:
Hello Sir,
I have a 1KVA automatic voltage stabilizer.It has one defect that when it is switched on, very high voltage is outputted for about 1.5s (therefore cfls and bulb got fused frequently) after that the voltage becomes OK.
I have opened the stabilizer it consist of an auto-transformer,4 24V relay each relay connected to a separate circuit(each consisting of
10K preset,BC547,zener diode,BDX53BFP npn darlington pair transistor IC,220uF/63v capacitor,100uF/40V capacitor ,4 diodes and some resistors).
These circuits are powered by a step down transformer and output of these circuit are taken across corresponding 100uF/40V capacitor and fed to corresponding relay.What to do in order to tackle the problem.please help me.Hand drawn circuit diagram is attached.
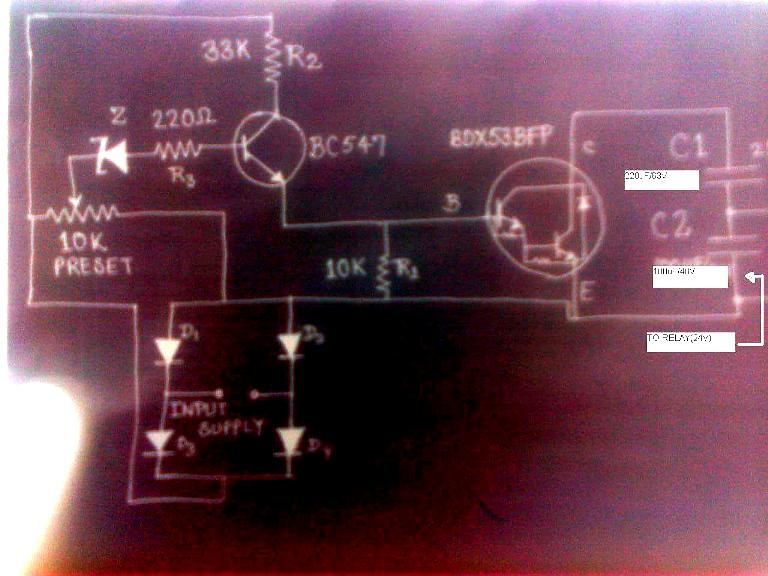
Solving the Circuit Problem
The problem in the above circuit might be due to two reasons: one of the relays is switching ON momentarily connecting the wrong contacts with the output, or one of the responsible relays is settling down with the correct voltages a little while after power switch ON.
Since there are more than one relay, tracing out the fault and correcting it can be a bit tedious......the circuit of a delay ON timer explained in the above article could be actually very effective for the discussed purpose.
The connections are rather simple.
Using a 7812 IC, the delay timer can be powered from the existing 24V supply of the stabilizer.
Next, the delay relay N/O contacts may be wired in series with the stabilizer output socket wiring.
The above wiring would instantly take care of the issues as now the output would switch after some time during power witch ONs, allowing enough time for the internal relays to settle down with the correct voltages across their output contacts.
Feedback from Mr. Bill
Hi Swagatam,
I stumbled across your page doing research on the web to make my delay more consistent.Some back ground information first.
I am a bracket drag racer and launch the car on first sight of the 3rd amber bulb as the christmas tree is coming down.
I use a transbrake switch that is depressed to lock the automatic transmission in forward and reverse at the same time.
This allows you to rev up the engine to build power for launch. When the button is released the transmission comes out of reverse and moves the car forward under high rpm.
This is like popping the clutch on a manual transmission car, anyway my car reacts to quickly and the result is a redlight, leaving to early, and you lose the race.
In dragracing your reaction time on the launch is everything and it is a game of hundreths-thousanths with the big boys, so I have put the transbrake switch on a relay and put a 1100uf cap combo across the relay to delay its release.
Because of the car electronics I don't believe there is a precise voltage charging this cap every time I activate this circuit and precision is key so I bought a power stabilizer off of Ebay that takes 8-15 volts in and gives a consistent 12volts out.
This turned my season around but i believe this circuit could be made to be more precise and to vary the delay time in an easier way rather than swap cap combos.
Also should I run a diode in front of the relay, not currently because all that is there is the on off switch- where will the current go? I am not an electrical engineer by any means but do have some knowledge from trouble shooting high end audio for many years.
Would love your thoughts- thankyou
Bill Korecky
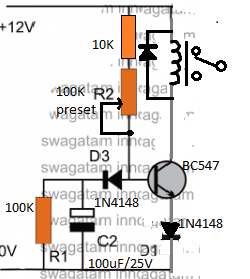
Analyzing and Solving the Circuit
Hi Bill,
I have attached the schematic of an adjustable delay circuit, please check it out. You can use it for the mentioned purpose.
The 100K preset can used and adjusted for acquiring precise short delay periods as per your specifications.
However, please note that, the supply voltage will need to be minimum 11V, for the 12V relay to operate correctly, if this is not fulfilled then the circuit might malfunction.
Regards.
Simple 5 to 20 Minute Delay Timer
The following section discusses a simple 5 to 20 minute delay timer circuit for a specific industrial application.
The idea was requested by Mr. Jonathan.
Technical Requirements
While trying to figure out a solution to my problem on google, I came across your above posting.
I'm trying to figure out how to build a better Sous Vide controller. The main problem is that my water bath has a very high hysteresis, and when heating from colder temperatures will overshoot about 7 degrees from the temperature at which power is terminated.
It is also very well insulated, with a gap between the inner and outer vessel which makes it act like a thermos jar, because of this it takes a very long time to decline from any excess temperature. My PID controller has an SSR control output and a relay alarm output.
The alarm can be programmed as a below limit alarm with an offset from the set-point. I can use a five volt supply I already have for my circulation motor to run through the alarm relay and drive the same SSR the control output is driving.
To be on the safe side and protect the PID controller I'll add a diode to both the alarm voltage and the control voltage to prevent one output from feeding back into the other.
I'll then set the alarm to stay on until the temperature rises above the set-point minus 7 degrees. This will allow the PID tuning to be adjusted without having to account for the initial temperature ramp-up.
Because I know that last few degrees will be achieved without any power input, I'd really like a way to delay any recognition of the control signal for about five minutes after the alarm shuts off, as it will still be calling for heat.
This is the part I've yet to figure out the circuitry for. I’m thinking of a normally closed relay in series with the control output, which is held open by the alarm signal.
When the alarm signal is terminated, I need a delay on the order of five minutes before the relay returns to its ‘off’ normally closed state.
I would appreciate help with the delayed off portion of the relay circuit. I like the simplicity of the initial designs on the page, but I get the impression they wouldn’t handle anywhere near five minutes.
Thank you,
Jonathan Lundquist
The Circuit Design
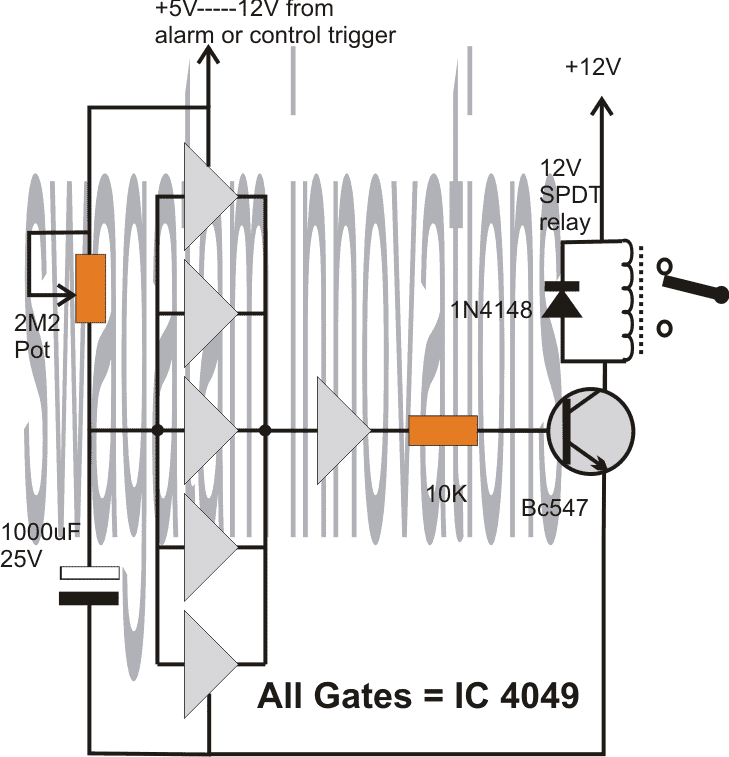
The following circuit design of a simple 5 to 20 minute delay timer circuit can be suitably applied for the above specified application.
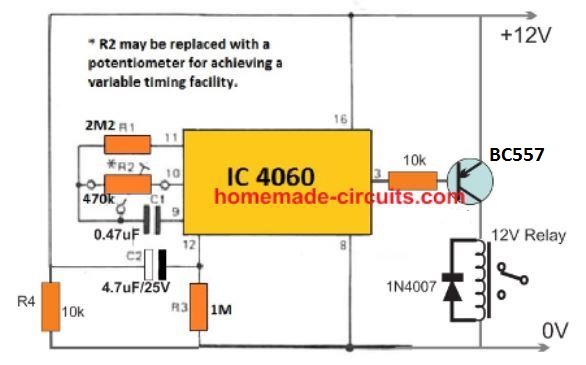
The circuit employs the IC4049 for the required NOT gates which are configured as voltage comparators.
The 5 gates in parallel form the sensing section and provides the required time delay trigger to the subsequent buffer and the relay driver stages.
The control input is acquired from the alarm output as indicated in the above description. This input becomes the switching voltage for the proposed timer circuit.
On receiving this trigger, the input of the 5 NOT gates are initially held at logic zero because the capacitor grounds the initial trigger via the 2m2 pot.
Depending upon the 2m2 setting, the capacitor starts charging up and the moment the voltage across the capacitor reaches a recognizable value, the NOT gates revert their output to logic low, which is translated as a logic high at the output of the right single NOT gate.
This instantly triggers the connected transistor and the relay for the required delay output across the relay contacts.
The 2M2 pot may be adjusted for determining the required delays.
Circuit Diagram

Hello Sir ,
No,not to modify anything in the stabilizer circuit,but to construct a different 5 seconds delay ON circuit board with its associated components and relay. I plan to pass the output of the stabilizer wire through the relay of the timer,so that when the stabilizer and the timer are powered ,the timer circuit switches ON output after 5 seconds. That is the circuit delays the switching ON of the stabilizer immediately when power ON switch is pressed.where do i tap the 12v to relay of the delay circuit. I hope i sound clearer now .Looking forward to your answer. Thank you.
So this delay is required only during the initial switch ON period… or during the entire voltage up/down fluctuations also??
helo mr swag,
I forgot to ask where i should i tap the 12v to suply the delay circuit from the stabilizer circuit board
Dear Mr Swagatam ,
Thank you so much for the above timer circuit.This is what i have been looking for.
Someone brought to me a Qlink stabilizer which couldnt enter delay to repair.I have concluded to use a timer switch to repair it by which the output wire of the stabilizer will pass through the relay of the timer circuit,to delay the stabilizer about 5 seconds.please i need the formular for the time calculation.
Should i go ahead or what do you suggest,Thanks.
Hi Patrick, do you want a delay ON circuit, meaning do you want to modify the existing relay inside the stabilizer with a delay effect of 5 seconds?
I would like to backlight a desktop calculator with el wire and a timing circuit. Is it possible to have the LCD screen trigger the circuit, switch on the el wire device and then turn off after 1 minute of inactivity? The wire is powered by 5v usb.
You can try the following one:
The Diode shown at the collector of the transistor should be replaced with the EL lamp, cathode towards the ground side.
The EL lamp will light up when it detects the LCD screen light, and will remain ON for a minute after the LCD is turned OFF
Hi Swagatam,
Nice work you doing here, answering all the guys with patience…
I tried to find the nearest related circuit to make it easier finding a solution.
I will try to use this in my bathroom to activate a fan which I need to run immediately as soon as it sees some light and switches off after the person left the room and switched off the light.
I am thinking of replacing the diode which you told to replace with the EL lamp by a Relais which will power the Fan.
My questions are:
1. am I correct if I increase the capacity of the 470uf capacitor to increase the time for switching off?
2. R5 is a regular LDR ??
Thanks in advance..
Thank you IŞIL AYLANÇ,
If you intend to use a relay as the collector load, then you can simply connect the relay coil parallel to the existing diode, and use its contacts to switch the lamp.
You are right, increasing 470uF will increase the delay OFF time.
Alternatively you can replace Q1 with two BC557 connected in Darlington mode and then increase the 27K value to 100K for getting a higher delay OFF time
R5 is an ordinary LDR
Hi, very interesting circuits. Can you help me to build a momentary switch activated by 220v or 12v please, after a few second??
I just need it to replicated a push button, and then Off, so disconnected.
Next 220v or 12v applied, the switch close itself again, after a few second delay, and again off.
Thanx
H, you can try the following customization
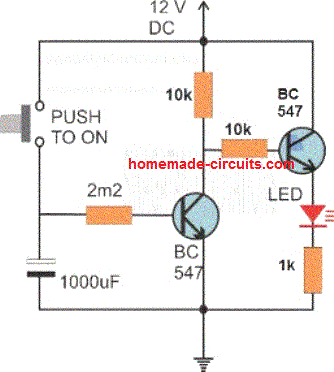
For loads other than the shown LED, must be connected beyween the positive and collector of the right side NPN….
Thx you, your site is a MUST for an electro lover!!
I will try the schematic you gave, and I read down that you also advise to try first circuit, just replace the 33k with a 0.22uF capacitor, and remove the 1000uF capacitor.
So I will give a shot to both and see which suits my needs.
Thx you very much!
Thank you, I am always glad to help!
Dear sir,
I required off delay adjustable timer circuit 0-1hour
Input 230v AC
Output 12v DC
With 555 or if any
Dear Kamesh,
you can try the first circuit from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/interesting-timer-circuits-using-ic-555-explored/
Adjust R1, C1 values appropriately to get the 60 minute delay.
great description and circuits.
I am try to make circuit in that, when we press button turn on led for some millisecond and turn off even if button is still pressed.
please help me on it.
Thank you, just replace the 33k with a 0.22uF capacitor in the first circuit, and remove the 1000uF capacitor.
Swagatam, look at the performance and mastery of the timed states, it seems they are your strong suit … I am fond of them, this delay for ignition plays in different projects, it is dynamic … hello, do not forget the washing machine type with delay of the start of the other turn … type washing machine …
I am looking to build a momentary foot pedal switch in a audio application. I am using a condenser mic which requires 48V DC. I would like to build a foot pedal that allows me to use a single xlr input but has two xlr outputs. 48V “phantom power” comes from the mixer via pins 2 and 3. I need to be able to add about a 5 millisecond delay when the switch is pushed in order to keep from causing a “popping” noise. Have you ever done anything like this?
I appreciate any help you can provide.
Do you want the delay for the 48V DC input or the music input? If it’s for the 48V Dc, it can be done, but not for the music!
I have been looking at another option that may be easier. If I used a constant 48V power supply upstream of a DPDT momentary switch that would keep me from having to use the mixer 48V power. the problem is that switching the signal from one channel to the other would possible cause a popping in the sound. is there way to stop the 48V from traveling back thru the switch? From what I have found, I sound be able to short the signal for the “off” channel to pins 2 and 3. I hope this makes sense.
I will have too see the schematic drawing to understand the positions of the signals, only then I can suggest a solution. A popping sound may possibly arise due to the sudden switch ON of the 48 V DC, not the audio signal.
If you want the 48V to reach the other side slowly or exponentially, then that can be done with a transistor capacitor and the popping sound could be avoided.
hi.
After energizing a dc voltage regulator, I want to open it a few seconds late.
how can I do that?
thank you.
which DC regulator?
MIC29302WT
try putting a 100uF parallel to R2
That’s great Dennis. To increase the timing you just have to change the 100k resistor to 1M….the other 1M resistors shouldn’t be changed.
Additionally you must also change the BC557 base resistor to 100k each…please do these changes you should be able to get the desired delay.
If still you are not satisfied then you can try the next circuit just below the circuit being discussed.
Thanks for informing, hope you succeed with the project soon!
Dennis, in the following circuit, both are NPN because here we are looking for a delay OFF effect, not delay ON. Meaning, the relay should be ON initially then OFF after the set delay is elapsed.
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/delay-off-timer.jpg
This circuit will allow you to get a more accurate control of the desire delay. You can easily get 30 seconds by adjusting the values of R2 and C2.
yes, it is wrongly printed as BC557 for the T2, which should be actually BC547
OK that’s fine, but for driving an SSR TIP127 won’t be required, you can simply use a BC557 instead, or any similar small signal PNP
Dennis, any SSR will require just a few mA to switch, which should not cause any loading on the driver circuit unless the supply current is too low, or the SSR itself is faulty.
You can also check if your SSR connections are correctly implemented, the (-) should connect with the ground, and the (+) should connect with the collector of the PNP transistor.
Thank you for the explanation.
As soon as i get some 10k resistors. I will give it a try and report back.
Sure, no problem!
An electronic device employs a timer circuit of a kind shown in figure. RC circuits are used to
create delay for alarm, motor control and timing application. The given circuit is part of building
security system. The input of the RC circuit is a 20 V and the capacitor value is 40 μF. When
the door is opened, you have a specified number of seconds to disarm the system before
alarm goes off. Determine the value of resistance required to create a delay of at least
25 sev ± 0.5 sec. The threshold voltage to activate the alarm is VC = 16V ± 0.05 V
Hello
I’ve built a muting circuit to mute audio on startup of an amplifier by grounding the outputs and then releasing the grounds once the circuit trips the relays. The problem is only one relay is activated, the other one sometimes works many seconds later or not at all.
Is there a way to post a schematic?
Hello, you can post the schematic on any free image hosting site and provide the link here, I will check it out…
Here’s a link to the image of the schematic.
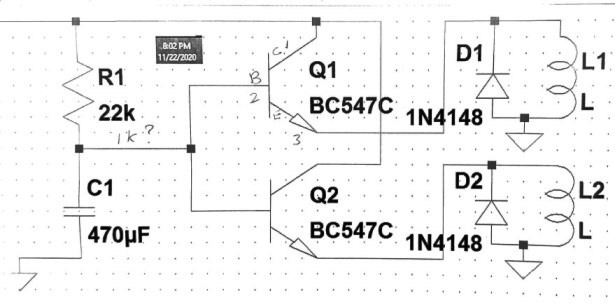
A relay should be always connected to transistor collector, not sure why you have connected them to the emitters. Anyway, in the present set up replace R1 with 10k, and add a couple of more 10ks one each in series with the bases of the two transistors, an see if that solves the issue….
Thanks for the reply.
I was following someone else’s schematic. So it’s ok with the relay coil connected to the emitter?
I have the 2 transistors on a stripboard with 2 bases on the same strip. Could i just use one 10k resistor going to both? If not I’ll have to redo the layout.
Using two separate base resistors ensures uniform sharing of the current and equal response from the transistors, if you use a single the condition may not show any improvement.
Ok so after marking those changes. I can hear the relays clicking between 7 and 10 seconds. Strange how they don’t all fire at the same time. Perhaps it’s just the relays? They’re 5v telecom replays and are brand new. I would like the delay to be 10-20 secs. How can i achieve this? Thanks for your input.
It is because the characteristics of the transistors will be always slightly different and will react differently to the relays. Additionally The relay resistances will be also never be exactly the same which may further add to the discrepancies.
I think you should go for a DPDT relay, which will enable you get a synchronized switching of both the relays. Otherwise you may consider shifting the relays on the collector sides for the same.
Good day Sir, please I need a circuit that when DC supply is given its relay is activated and deactivated immediately. Thanks Swag
Seun, just connect a 47uF capacitor in series with the relay coil, and a 22k resistor parallel to this capacitor, this should fulfill your requirement…
Thanks Sir, it worked, but how can I make the on and off 3secs interval for the relay push button.
Glad it worked seun, the value of the capacitor determines the ON/OFF delay time, higher values will give higher delay time and vice versa
Thanks Sir for this article, I tried the “without push button” circuit, but it was was even on for more than 10minutes and never became deactivated ‘forever’ I don’t know why is not going delay off .
I want a without push button circuit, please help out.
Seun, you can try reducing the 1M base resistor to 100k or lower and see the effect, or you an also try reducing the value of the 1000uF to 100uF
No I have not built the circuit. I have been busy with other things. I will let you know as soon as it is built. Thanks.
Okay!
Thank you, I will try that and get back to you.
Bob.
Hi,
Like most people I am flicking through the internet looking for a solution to a particular problem.
I want to monitor a train on a model circuit, when it goes over a sensor (in this case one track connected to the other by the train wheels, the common rail has 0v on it so the input to the circuit would start its timer when it sees a 0v signal) nothing happens initially when the train leaves the section and the signal is no longer there then a relay is closed for a second (after a short delay, say 3 seconds, to cover for a dirty rail).
The way I am trying to do it is to charge a capacitor and keep it charged while the signal is coming from the track, if the wheel misses for a second the capacitor would start to discharge but it will see the signal again and recharge so not get to the point when the relay closes till it has seen no signal for about 3 seconds.
Would the delay on timer circuit above do this?
Thanks.
Bob.
Hi, I have never used a model train, so I am having difficulty in understanding the situation, there are many things which are not clear, like, where should the circuit be, inside the train or outside the train, what is a dirty rail? what is the wheel supposed to miss and where?
Alternatively, if you can explain how you want the timer circuit to work, or the specifications of the timer circuit, It would help me to understand the situation better!
Thank you for the reply.

What I am trying to do is produce a small circuit that receives a 0v input from a garden railway.
The system works on 24v and has a number of small circuits consisting of a resistor and relay in series like this.
The relays I am using have four sets of contacts, the other three are used for changing the signals from green to red and back.
Points A and B are connected to one rail, the other rail is connected to 0v. A train goes over the point A and connects the bottom of the relay to 0v, this energises the relay. As the relay coil signal goes through one contact the coil is now latched on. When the train goes over the point B it puts 0v on the top of the relay and the relay de energises.
What I would like to happen is the train crosses point A and a 0v signal is sent into a circuit, if the 0v stays on (or keeps appearing because due to dirty rails the signal may not always pass cleanly, there may be a break of, say, half a second) then there is no output from the circuit, i.e. a capacitor keeps getting charged or discharged. When the train leaves point A the capacitor gets the chance to discharge or charge far enough to produce a signal that will show on the relay to energise it. This will indicate that the train has passed the point A and moved to a point between point A and B. A similar circuit could be used at point B to do the same thing.
OK thank you for explaining in detail,
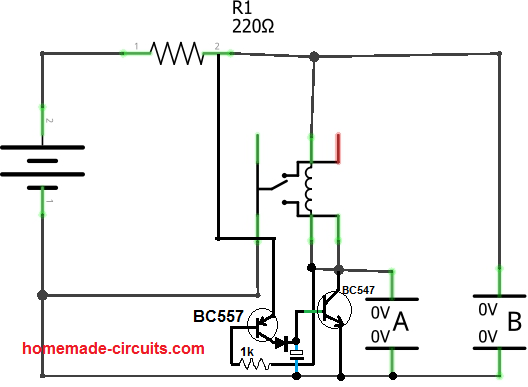
I think I got it now.
You can probably do the following modification to your existing circuit:
The base diode can be a 1N4148, and the capacitor can be a 1uF
My fridge at start up draws much power. i need a simple circuit design to control it from getting damaged as i feel it may. pls is it adviceable to keep using the fridge that way or to get a deigned circuit to cause a delay of inflow power in it?
Thanks
Ugo
That looks quite normal to me, fridge motors or any other motor will always draw higher current at the start up. If you prohibit this it can cause malfunctioning of the system
Hi and thanks for such an informative article. I’d like you to please help me with this, at it seems I’m not able to get a solution.
There is a microprocessor that needs a delay to be set when being powered up. The BE line needs to be switched from low to high 100 ns after the RESET line.
I explain again: when being powered up, the RESET line switches from low to high (0 to +3.3v). And 100 nanoseconds *later* the BE line also needs to be switched from low to high.
How can I achieve that
Thanks.
Hi, thanks, you can apply the +3.3 V to the BE line through a PNP transistor and delay the transistor conduction through a resistor/capacitor network at the base of the transistor
Hi there,
I’m not sure if this is entirely relevant to this article, so apologies in advance, but looking for input/ideas from someone that knows far more about electronics than I do! I’m wondering whether it would be theoretically possible to do some of the things mentioned above for a potentiometer (for an analog stick on a video game controller). Essentially, I’m wondering whether its possible to create a circuit where moving the stick (say to the right) will register an input for a very brief window (say 1/60th of a second) before instantly returning it to the neutral voltage of the potentiometer (as if the stick was in its neutral position) despite still being held. Then, when the stick is released physically, it would be ready for this process to repeat. This essentially would work to eliminate the “hold” input of the stick and simulate it being a very precisely timed button press.
Sorry, I’m aware this is a very poor explanation; I’m not an electrician! This is more of an academic interest with a mind to modifying my hardware if its within the realms of possibility!
Thanks very much for reading!
Hi, do you mean creating a momentary time delay pulse of 1/60th second through a pot movement at its extreme end?? Yes that can be done through an op amp attached with the pot resistance..
Hi again Swagatam
Having now completed a timer circuit based on your design, I now want to build a door alarm circuit that will be triggered by the opening of switch (maybe a reed switch).
This will set of an alarm by the operation of a relay for a set period (maybe 30 seconds) then it will turn off.
I see that you have done circuits for the above however using the 555 but I cannot see one that will fit this final requirement.
That is, once the alarm has completed its operation, then I do not want it operating again, even if the door (reed switch) is left open or is closed or opened again. The circuit can only be reset by manually operating another switch.
The circuit can run off a voltage of 9 – 12 dc volts.
Regards
Dave
Hi Dave,
You can try the second circuit from the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/loop-alarm-circuits-closed-loop-parallel-loop-series-parallel-loop/
You can eliminate the extra switches S3, S4, and replace S2 with your reed relay.
The SCR can be a C106
If you want the reset switch to be a push-to-ON type, then you can use the same in parallel to C1, and replace S1 with a wire link.
Hi Swagatam
Thanks for the quick response.
I understand that the alarm will be audible until such time the reset switch is activated in this circuit. However I maybe didn’t make it clear that I only wanted the alarm to be audible for around 30 seconds and then turn off. Then it would require the manual reset switch to restore the circuit back to its normal state where its waiting on S2 to open.
Regards
Dave
Hi Dave, I got it, you can try the following circuit with some modifications:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/Fig-2.jpg
Replace the switch S1 with the anode/cathode of an SCR.
Next connect the reed switch across the positive line and the gate of the SCR, and connect a 1k across agte and ground of the SCR
Hi Swagatam, I’m slightly confused about the reed switch going between the +ve rail and the gate of the SCR. Because the Reed switch will be normally closed when the door is closed, which will mean that a positive voltage will be applied to the gate of the SCR turning it on and causing the 555 at 3 to go high and activate the alarm. Or have I got something wrong?
Regards
Dave
Hi Dave, In that case, simply reverse the configuration. Connect the reed between SCR gate and ground line, and connect any resistor between 1k and 10k between gate and positive.
Hi Swagatam,
Ok, I have now tested it and found the following.
When the reed switch opens the SCR latches and applies a low state to pin 2 of the 555. Then Pin 3 goes high and operates the relay. All good so far. At Pin 6/7 the voltage then gradually rises until it exceeds the 2/3 supply voltage. But Pin 3 stays high and the relay does not release.
Is this because the SCR is still latched until the supply voltage is disconnected, so it will continue to supply a low state to Pin 2?
In a separate test with the reed switch closed and the SCR not latched, I momentary applied a low state to Pin 2 and the relay operated then released after the timeout. All good.
If the SCR being permanently latched is causing the relay not to timeout, then what I would like is for the relay to operate after the reed switch opens then for the relay to release after the timeout period. Irrespective of how many times the reed switch closes and opens during the timeout period or after the relay releases. Its only by removing the power supply and reconnecting the supply that it will restore the circuit to normal.
Look forward to your thoughts on this.
Cheers
Dave
Thanks Dave, I think the following modification in the previous diagram should perfectly take care of the issue that you facing.
The capacitor in series with the pin2 of the IC ensures that the latching of the SCR does not have any effect on the pin2 of the IC 555
Hi Swagatam,
Ok, I bread boarded the 4060 circuit as you suggested as follows: The positive for the KD9561 alarm is connected to the positive rail. The negative of KD9561 alarm is connected to pin 3 of the 4060. The LED is connected from positive rail to pin 4 of the 4060. The 4060 will not sink enough current to play the KD9561 alarm, so I added a PNP transistor. Pin 3 of the 4060 is connected to the base of the BC327 PNP transistor with a 1K resistor. The negative of the KD9561 alarm is connected to the emitter of the BC327 PNP transistor. The collector of the BC327 PNP transistor is connected to ground. When power is applied, the KD9561 alarm sounds until the 4060 times out and the diode latches it with a high output from pin 3 of the 4060. The KD9561 alarm stops and the LED stays lit, which is correct. I can add my delay-on 555 circuit to allow powering on the circuit without the KD9561 alarm sounding, but I still need a way to only turn on the 4060 when LIGHT is present. I haven’t been able to find any example circuits using LDRs to activate a 4060 IC. Maybe I’m missing something. Assistance please. Thanks!
Hi Norman, for LDR triggering, connect pin12 of the IC to ground through the LDR, and also connect a 220k from pin12 to the positive line.
Hi Swagatam,
I really don’t understand your last comment with respect to the cd4060. So, I used the first 555 delay circuit to allow powering alarm without the alarm sounding on power up. I then used your 555 one shot circuit to allow the alarm to activate with light and sound for a preset time and then not re-alarm when light is present again. I then used your transistor latch circuit to latch a flashing LED, which indicates the alarm has been tripped. The circuit works good and I am sending you a schematic by email. Thanks again for you help!
Hi Norman, If you connect the IC 4060 exactly as suggested by me, you would be able to get all those required features through a single IC.
Yes, exactly!
This can be achieved through a single IC 4060. Use its pin3 to activate the buzzer, also connect a diode from pin3 to pin11 for latching the buzzer.
The buzzer should be connected across positive line to pin3. The LEd could be wired across pin4 and ground for getting the flashing effect.
Hi Swagatam,
OK, I am still working on the Refrigerator Alarm. The delay circuit and your one shot circuit work fine. I wanted to add a latched LED (Flashing type) to indicate that the alarm had been triggered. I have tried several circuits with no success. The most promising looked to be using a BT169. I connected it with a 10k resistor from the transistor pair from pin 3 to the gate. I connected the LED from 5v to the anode and connected the cathode to ground through a 2k2 resistor (to protect LED). It works until the 555 times out and then the LED is off as the alarm is off. If I remove the 1uF capacitor from the circuit, it works. The LED flashes even after the 555 times out. which is what I want. It indicates the alarm has been triggered. The problem is ,without the 1uF capacitor, the alarm will sound anytime it receives light. So when the mother comes home and opens the refrigerator door, the alarm sounds and she has no idea if the kids have been in the refrigerator. I am sending by email a schematic of my circuit. I hope this is not aggravating you. Thanks for your help!
Hi Norman, do you mean the whole circuit should be latched and “frozen” when the door is opened by the child, until reset manually.
So when the child opens the fridge door, the alarm sounds and latches the LED. Next, when the mom opens the door the alarm does not sound, and the mom sees only the flashing LED, realizing that the fridge had been opened before by someone.
Hi Swagatam, I found a delay ON circuit that works. It is another 555 circuit that has pin 7 not connected. Pin 2 and 6 are shorted together. A 470uF cap in connected to pin 2 or pin 6 with the negative leg and the positive leg connected to VCC. A 47K resistor is connected from pin 6 or pin 2 to ground. When the circuit is powered the capacitor keeps pin 2 positive until the cap reaches a point and stops transferring to pin 2. The 47K resistor allows pin 2 to be grounded and then pin 3 goes high. Pin 3 is connected to the base of a BC548 with a 1K resistor. The emitter of the BC548 is connected to ground. The collector of the BC548 is connected to the base of a BC327 with a 1K resistor. The emitter of the BC327 in connected to VCC. The collector of the BC327 is connected to the positive rail of the circuit you gave me. The negative rails are common. I tried this with out the transistor pair and it worked, but was weak, so I added the transistor pair. I also added the same transistor pair to the output from your circuit as it provided a little more power to the music siren chip. I love your circuit. I tried to find it on your site so I could understand exactly how it works, but I couldn’t find it. Would you mind explaining how your circuit works. I understand some of it but the diodes are confusing to me. Thanks again for your quick response. You are the best!
H Norman, that looks just the opposite of a monostable operation. As long as the capacitor keeps the pin2 high, the output pin3 remains low, and as soon as the pin2 becomes low, the output pin3 is pulled is high permanently.
Hi Swagatam,
The circuit you suggested works great for the delay off for the alarm. What would you suggest for the delay on part of the circuit? I need to be able to power on the circuit with a delay so I can place it in the dark space without the alarm sounding prematurely. Thanks!
Hi Norman, You said that
“the alarm would be powered on and placed inside of the refrigerator. when someone opens the refrigerator door, the alarm would sound and if they close the door, the alarm would continue to sound for say 1 minute. and then would shut off and not reset”
The 555 circuit would do exactly the same…. I cannot see the delay ON action need anywhere in your requirement…
Initially, for the first time the alarm will sound while installing the system inside the fridge, but once installed, the 555 circuit will sound only when someone opens the fridge door.
Hi Swagatam,
I forgot to mention that I will be powering this circuit with 3 AAA batteries. The chip will work on 3-4.5v
Hi Norman, if you apply the circuit suggested by me, you can use a CMOS IC 555 and use a 4.5V comfortably.
Hi Swagatam,
I have been working on an alarm that will drive a prerecorded Chinese music alarm chip. The alarm chip needs clean 3v to operate correctly. The alarm would need a delay when power was applied so the alarm module could be placed. The alarm would need to be activated by light. For example, the alarm would be powered on and placed inside of the refrigerator. when someone opens the refrigerator door, the alarm would sound and if they close the door, the alarm would continue to sound for say 1 minute. and then would shut off and not reset. The circuit would have an led to indicate that the alarm had been triggered. This led would be a flashing red led and would only light when the alarm had been triggered. I built the alarm with a LM358 using one side as the alarm trigger and the other side as the delay. I tried adding your latching transistor circuit and it worked. The problem with my circuit is if you block the LDR the alarm goes silent and it doesn’t shut off after 1 minute. Once the time delay is over the circuit remains high forever. I have the output from the LM358 feeding a NPN transistor that grounds a 555 one shot, but it never shuts off due to the input from the LM358 being continuous. I tried adding a 0.1uF capacitor with resistors on both sides to the positive rail and it still would not shut off. The grounding resistor from pin 2 of the 555 is driven from pin 1 of the LM358. Do you think you will have time to design such a circuit and post it on you site? Thanks for your assistance.
Hi Norman, I don’t think op amps would be required for the application, you can probably use the following 555 monostable for the purpose:
The LED can be added in parallel to the speaker for the blinking effect.
Please how can I restart the 2nd circuit without discharge the capacitor, because it works first, but doesn’t restart after reconnecting without shorting the capacitor to discharge it
The answer is given in the transistorized version presented in the following article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-long-duration-timer-circuit/
Hello, Good morning…
Wow, lots of questions and comments.
I’m trying to find one of your designs and suggestions in here to power a computer ON and OFF with a IR remote. Not sure if this is the best way the go, but i would like to find out if possible.
The computer power button use 5v, when pushed it shorts the connection (like 0.5 sec needed).
Could you suggest a best option/design to accomplish this, please.
Or you think will be best to go a different route like using a 555 or perhaps an Attiny85 mcu, or ???
I have see many circuits, getting confuse which way to go.
Thanks a lot for your time and any suggestions.
Good Day
Hi, if you are sure about 0.5 second ON/OFF trigger for the button start then it can be easily done with a 555 IC based IR remote control or even an ordinary RF remote control, which looks more convenient since the whole module can be cheaply procured. In fact the momentary ON/OFf system is already included in those systems.
I sincerely appreciate your circuits for the delay on or the delay off. Would it be possible to show a circuit that does both – a 3 second delay on (no momentary switch) before turning on the led and also supports a 3 second delay off (when the power of 3v is turned off) before turning off the led? Not looking to cycle the on-off but instead support a one time delay on and if on long enough to charge the capacitor, also support a delay off. Would this be possible with the fewest electronics?
It can be probably achieved with the second design through some minor modifications, as I have explained below:
The switch points should be shorted. The 2m2 should be replaced with two series 1M resistors, and the capacitor should be placed across the junction of these two 1M resistors and the ground line.
For an enhanced effect, the emitter of the NPN could be connected to the negative via a 1N4148 diode
Thank you Swagatam for the super fast response.
Two questions:
1. For the first two diagrams, I was able to get them to work perfectly at 12V. Very nice. What would change for only 3V (actually 2.1 to 3V) rather than 12V? (This application uses two AAA batteries that may be rechargeable to drive the led, hence the low voltage).
2. I tried making the changes you suggested to the second diagram but when I move the capacitor to the junction of the two 1M resistors, the led fails to go on at all. If I move the capacitor back, only the delay off portion works as before but no delay on. Would it be possible to email a diagram that supports both a delay on and delay off that works for 3V?
If the requests are out of line, no worries, please let me know and again thank you for all your help.
No problem Bob, however the two resistor and a center capacitor network should definitely work, regardless of the supply voltage.
You can try reducing either the resistor values or the capacitor value and check the response, you may find the circuit working exactly as per your required specs.
For 3 V the emitter of the NPN must be directly linked with the ground without a diode.
HI Swagatam
Is there a circuit you can provide that will do the following please?
1. I want a relay to operate when my cars ignition (+ve 12V) is turned on.
2. The relay is to remain on for around 5 seconds, then it will release.
3. It will not then re-operate due to the ignition switch still being on.
4. It will only operate again once the ignition has been turned off, then turned back on again at a later time.
Thanks
hi Dave, you can apply the first circuit from the following article with a little modification:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/input-trigger-synchronized-monostable/
Please connect a 10uF/25V capacitor across the points labeled as “Left Pins”
That’s all.
You will also have to adjust the values of R2, and C1 to get the required 5 seconds precise output
The 12V supply to the circuit must come from the ignition switch
Excellent, thanks so much Swagatam for that and for coming back to me so quickly.
I have now got all the components and will put it all together in the next couple of days.
Cheers
Dave
That sounds great Dave, let me know if you have any problems!
Hi again Swagatam,
Made up the circuit on a spare bit of Vero board I had, then tested it’s functionality under all conditions. And the verdict….perfect!
Thanks again Swagatam
Now all I have to do is wire it into the car.
Thanks Dave, and glad you could build it without any issues, hope it works in your car also.
dear sir i have made above IN4148 circuit. with 2N4401 and 2N4403 transistors. but LED is always on when power supplied. any reason for that sir?
Hi Jayanath, are you referring to the second design? It requires a push button, which is pressed momentarily and released, which keeps the LED illuminated for sometime then shuts it off. If you keep the NPN base permanently connected to the supply then the LED will stay always ON
Dear Mr. Swagatam
Appreciate your detailed responses and feedback to each query received.
I need help with the following application.
A 220 VAC load needs to stay off for a 15 second delay and then stay on for 30 minutes. This should happen on switching on a main power supply to the load.
Pls do help me with the correct circuit for the same. The application is Industrial in nature. The load current is not high (1A) and can be switched via a PCB mounted relay
Thank you Dear R Fernandes,
you can try the following concept:
C2/R3 decides the delay ON time (15 seconds)
C1/R2 decides the OFF time.
I forgot to add a 1N4148 diode across pin3 and pin11, so please add it. Cathode will go to pin11
The timing parts are arbitrarily chosen, so you will have to tweak them to perfection with some trial and error.
Dear Sir
Your promptness and attention to detail are impeccable. Thank you very much for the help. Will have this tried and will revert with feedback once the markets open here for component procurement.
Best Regards
No Problem dear Fernandes, please feel free to revert if you have any problems or doubts regarding the project, I’ll be happy to help!
Hi Swagatam,
I am looking for a circuit for my DIY hand sanitizer. Could you please help me to figure out this issue.
Power supply for this circuit is 12V (because I am using 12V pump).
The input is from an IR obstacle avoidance sensor that will produce 0V when detecting hands and 12V in normal condition. The function is as following:
1. Pump is in standby mode.
2. When detecting hands, pump is activated immediately and running in 2 seconds.
3. After 2 seconds, pump is deactivated in 3 seconds (this will prevent pump working continuously), even IR sensor detected hands or not.
4. After 5 seconds (2 seconds activated and 3 seconds deactivated), if detecting hands go to step 2, if not go to standby mode.
I attached a diagram for better understanding.
https://photos.app.goo.gl/NCCPTeyArYRLCruh7
Thank you and hope to receive your feedback.
Rgds,
Muoi
Hi, I bought a 240v ac adjustable electronic repeat cycle timer, when buying it I didn’t realise it was 240v ac as I need 24vdc. I can supply 24vdc to it and get it working but the moment I put any load on the output it instantly drops from 24vdc to almost no volts. Can anyone please let me know what needs to be done to the pcb to fix my issue. I can supply photos of the pcb if needed. Thanks
If you apply 24V Dc in place of 240V AC it won’t work. You must find out the operating DC of the circuit and the supply lines of the PCB, and then apply the specified amount of DC across the DC supply lines of the board via a protection diode.
Hi Swag –
I’m looking for a Power-On Timer solution that may be a variation of the Section 2.3 Without-a-Button circuit. I’m powering a 12VDC 2A (sustained) solenoid. I would like the solenoid to activate when power is applied (no trigger button) and stay on for at most 10 seconds (6-10 seconds set via RC would be okay). The solenoid would then deactivate, even though power is still applied, until power is removed and then reapplied. If power is removed before timeout, the solenoid would deactivate (expected because there’s no power). I like the 2.3 circuit but I’m wondering if it could be done with just one transistor since the delay is less than 10 seconds. I prefer a transistor/triac/opto output and not use a relay (for reliability due to sparking). I will/can put a flyback diode across the solenoid coil since it does have some bite on discharge! Any ideas? Thanks!
Hi Ron, you can use a single transistor, a Darlington type such as TIP122, or TIP142 for a higher current load. You can also try a MOSFET such as IRF540 for improving the results.
Sir can you give a schematic diagram for this? How to connect MOSFET in the said circuit? I also need an automated spray (no switch button) the spray will be on due to the PIR sensor. The process must be, when the PIR sensor detects a person in front of the door, theres a 5-10 seconds delay to trigger the dc pump which will cause the spray. And i need the spray to be on for 3-5 seconds before it turns off.
Hi Jill, you can try the following schematic:
I forgot to show a 1K resistor across gate/source of the MOSFET. So please add it. The 10uF will need to be tweaked appropriately for getting the mentioned delays.
Sir can I ask on how this works? Like can you explain what happens to every component on this circuit? I wanted to know the working principle of each components. Thanks sir
When PIR detects humans, it sends a positive bias signal to T1 base, but due to C2 T1 does not conduct immediately. When C2 charges fully T1 conducts, which switches ON T2, the MOSFET and the solenoid.
When the human leaves, T1 stops conducting but T2 continues to hold the solenoid until T2 base capacitor discharges fully.
Thank u sir. But how did you come up with the certain values of capacitors and resistors? Also sir what specific model of transistors should I use for the BJT and MOSFET. Like their max current and power rating (I have no idea on this)
I have selected them approximately due to the wide tolerance range for transistors. The base RC decides the time delay with respect to the collector load. The basic formula can be studied in this example article:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/universal-high-watt-led-current-limiter
Also sir If i were to use a dc pump what the minimum or maximum ratings should i consider? Like its min/max current, voltage and power?
I have not yet investigated charge pump circuits, so can’t suggest about it.
Sir do you know any other simulator application? I’ve tried Proteus 8 using the circuit u gave me, but it does not run the circuit. It says “AVR: Program property is not defined” and also “Real time simulation failed to start” because due to quarantine, we cant try it with the components. Hope u could help me sir.
Jill, build it practically with real and good quality components, you will get the desired results without fail. I have never used simulators because I feel they are far inferior compared to a human mind simulation and tests
Yes ur right sir, but due to the quarantine we cant go out and buy such components.
Sir is my explanation correct with regards to the working principle of the circuit “When IR senskr detects a motion, it sends a positive bias signal to T1 base, but because of C2, T1 does not conduct immediately. The RC network plays the role for the delay on timer because when the IR sensor detects motion, current begins to flow into the capacitor via the resistor, the capacitor gradually charges up through the resistor until the voltage across it reaches the supply voltage of the battery, and the resistor reduces the flow of current to the capacitor to slow down the time it takes to charge the capacitor. Then, when C2 charges fully, T1 conducts which switches on T2, the MOSFET, and the DC Pump. In addition, T1 will stop conducting but T2 continues to hold the DC Pump until T2 base capacitor discharges fully which is responsible for the delay off time.” Hope you could confirm it sir if my explanation is accurate. Thanks a lot!
Hi Jill, Yes your explanation is correct, except the C2 charging, which has to charge only up to 0.7 V to switch ON T1, rest everything is correct.
Sir why did you use transistors? Did it act as a switch? Why use transistors in that circuit? What is its purpose? Hope you can explain it to me
Thank you
Yes transistors are used as switches. When the base voltage rises to 0.7V across base/emitter, the collector emitter switches ON. The delay in reaching the 0.7 V level is controlled by the base resistor capacitor values.
Dear Swagatam . Could you please help me? second circuit (Delay off timer with BC547 and BC 557) . If i use 6 volt DC and If i change the LED and RESISTOR with a 6 volt relay (120 mA of coil) would it work?
thank you.
Dear Vahid, yes definitely it will work.
Hi,
I need a circuit 1 or 2 for driving a Picaxe micro processor (14M2/28X2, approx. 5v supply) and keep it running for about a little more than 80 sec. after interrupting the supply. That seems far off the values in your circuits. Can you suggest values to experiment with?
best regards
torben
Hi, you can try the 2nd circuit from this article…you can get even up to 5 hours delay by suitably adjusting the 2M2 and the 1000uF capacitor values
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/how-to-make-long-duration-timer-circuit/
Can I request a circuit where you push a button then ON and OFF are delay powered only with 3v 2032 cell
And also a Delay ON powered only with 3v 2032 also.
Thanks..
Cheers Swagatam!
Thanks Zerfallen, all the above circuits are rated to work with 3V and above, you can use them as per your specifications.
Hi Swag
Greetings from South Africa. Thank you for the informative article. I need to pick your brains for a little project I am trying to put together for my kids. I am a chemical engineer, so electronics are not part of my comfort zone. So “Idiots-Guide-Style” answers would be appreciated.
My kids practice fencing and I want to put together portable signal boxes that would register when they manage to score a hit on their opponent. They are using epees where the tip of the sword acts as a push button switch, normally open. I am cabling the sword’s body wire to a 9V battery powered circuit. The idea is that a closed circuit lights up an LED and sounds a buzzer.
I had the circuit all worked out with LED, buzzer and the relevant resistors and was going to test whether it would work better in a parallel or series configuration. Then it dawned on me that the circuit would only function as long as the tip of the sword was in contact with the opponent, which would only be a fraction of a second.
So what I need is a circuit that would allow the LED and buzzer to stay active for 2 second or so after the switch has re-opened. The first circuit you showed, with the single transistor, would seem to fit the bill, but I have no idea which transistor and capacitor to use. I also do not know if a capacitor can charge up in the short time that that the sword tip would close the circuit.
The other idea I had was to have the sword tip activate a 555 timer which would then let the LED/buzzer come on for 2-3 seconds. Problem is I have no idea which 555 to use. The LED’s are C515, 30 mA for the one indicator box and D105, 20mA for the other. The buzzer is a 5V, 25mA max unit. Resistors are R1 5W for the series option and R47 0.5W for the parallel option.
Could you please give me some advice on what would be the best type of circuit to put together for this application?
Thanks Nils,
yes you can use the first simple circuit. For the capacitor you can use a 100uF/25V, and for the resistor you can test different values from 1M and downwards, until it gives you the required 2 second delay OFF timing.
You can also use an IC 555 based monostable design as shown below:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/intruder-alarm.png
Ignore the 2M2 resistor and the LDR. The input trigger can be applied to the transistor 10K end. Also connect a 10K across the base/emitter of the BC547.
Thanks a stack for the detailed response.
On the first simple circuit, where should I put the 5V buzzer?
If I understand the intruder alarm circuit you posted correctly, I would leave out the LDR and replace the 2M2 with the connection to the epee tip. Two question I have is where would the LED fit in, and to connect a 10K over the base/emitter of the BC547, can I simply put it in place of the LDR or must the base connection be between the existing 10K and the base?
In the first diagram, you can add the buzzer in place of the LED/resistor.
In the 555 link, after removing the 2M2 and the LDR, the 10K end of the transistor can be applied with a momentary positive trigger for activating the 555 output. The external trigger source negative and the 555 negative must be linked in common, otherwise the 555 won’t respond….same applies for the transistor circuit also.
The other 10K must be across the base directly and the ground line, not in the LDR position.
I have drawn up a diagram of an adaptation of the first circuit. Is there any way I can send it to you to see if it would work?
You can upload it in any “free image hosting site:”, and provide the link here, I’ll check it.
Good day swag I am a solar IT student and am working on a solar powered water level indicator this indicator have the ability to auto switch ON/OFF the pumping machine and alarm to alert the use that the water un the over head thank is full. The alarm peeps continuously so am trying to control the alarm at least to peep for like 30min to 40min. Pls can you help me with a solution on how to add a delay timing ic on the circuit to control the alarm. Thank you.
Hi Joseph, can you please provide the details regarding how the alarm stage is switched ON from the control circuit? Is it through a HIGH output logic or a LOW logic, and what is a specifications of the alarm device…Once I know these I’ll b able to solve it for you.
Thanks for putting all this together, its been very helpful for furthering my understanding.
I am trying to put together a project involving a raspberry pi running on a battery, charged by solar.
I want the raspberry pi to turn off when either the battery gets low or the solar panel is actively charging. The charger I am using has an output pin that turns on under exactly those circumstances, and I believe I can use that on a GPIO pin on the RPi to request a safe shut down. But when the RPi is “shut down” it apparently still draws like 100mA, which is far too much for how thin of a line I am walking with charging and power consumption on this project. The voltage booster between my battery and my RPi has a pin that will allow me to turn off power completely, but if i just cut power to the RPi it can cause corruption.
So I need to be able to request an orderly shut down via the GPIO pin, then wait long enough for the pi to turn off, and then cut its power completely.
Then, when the solar panel turns off, I want that to trigger the RPi to turn back on. I think I have figured out how to do that with 3 relays, but I think one of them needs to have a short delay.
It seems like some of the circuits you’ve described might be exactly what I need, but I’m so far out of my depth I can’t tell which one or how I would need to apply it to my situation.
Any advice would be appreciated.
Thanks Kyle, glad you liked my posts.
I tried to understand your requirement, but I am having difficulty in getting and executing the stages together in my mind.
However, if you are looking for a delay timer that would switch ON a desired relay after some predetermined delay, this can be simply implemented using the following concept:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/delay.png
This will switch ON the relay after some delay as determined by the values of the upper 100K, and the capacitor
With the arduino based inverter circuit, is it practical to use the arduino to control the relay rather than a delay circuit? In the software, maybe after the first full loop turn the relay on?
No it won’t be a good idea, because we don’t know how the Arduino outputs would respond while booting…it could begin with both the outputs ON.
I have a question, how can i activate a simple delay timer with a relay that designed for 12 volts by 24 volts .Can i change the values of the resistors by doubling there values and change the relay to 24 volts keeping the RC time same thanks
You can do that, but doubling the resistor may not necessarily produce the same delay.
Please sir I want you to suggest a simple circuit out of these to on for 5secs and off for 5secs continuously. Thanks
Hi Favor, these are one shot timers, you will need an astable, as given here:
https://www.homemade-circuits.com/timer-ic-555-explained/#How_Astable_Mode_Works
HI, I’m new to electronics but have played around with 12v relays and LEDS for various projects for awhile. I came up with a project to make an automatic chicken coop door. I used a pre-built light sensor relay to open and close the door via double pole latching relay (relay acts to forward and reverse the motor to the door) My issue is the chickens never get in on time and often 2-3 are trapped outside looking through the perspex door. I have been researching using IC555 chip along with a IC4020b to make a timer (standard flexi/interval timer project). I stumbled across your site and thought I could adapt the “delay on” circuit I just need to incorporate an LDR so it delays about 1hr after dark to move the relay from NO to NC and then during the day the LDR allows the relay to go to NO. I know I need a configuration of an LDR and transistors to make this work, could you offer any advice.
Hi, for the mentioned requirement you can modify the delay ON timer by including another BC547 transistor. Connect its collector/emitter across R1. Next connect its base at the junction of an LDR and a 100K resistor. The LDR will be on the positive line side while the 100K will be at the ground side.
When the light is insufficient on the LDR, the BC547 will slowly switch off allowing C2 to get charged via R2, and finally switching ON T1/T2. The relay will be at N/C during day time, and at N/O during night
Thanks, I’ll go buy the bits tomorrow and give it all a try. Hopefully have happy chickens before the weekend.
Sure, wish you all the best!